Bucket sort
| EN | CN |
Bucket sort, or bin sort, is a sorting algorithm that works by distributing the elements of an array into a number of buckets. Each bucket is then sorted individually, either using a different sorting algorithm, or by recursively applying the bucket sorting algorithm. It is a distribution sort, a generalization of pigeonhole sort, and is a cousin of radix sort in the most-to-least significant digit flavor. Bucket sort can be implemented with comparisons and therefore can also be considered a comparison sort algorithm. The computational complexity depends on the algorithm used to sort each bucket, the number of buckets to use, and whether the input is uniformly distributed.
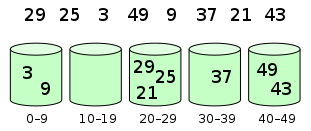
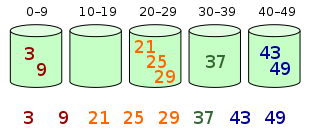
Bucket sort works as follows:
- Set up an array of initially empty “buckets”.
- Scatter: Go over the original array, putting each object in its bucket.
- Sort each non-empty bucket.
- Gather: Visit the buckets in order and put all elements back into the original array.
Source code
桶排序
是一个排序算法,它的稳定性取决于你在桶内使用的排序算法。工作的原理是将数组分到有限数量的桶子里。每个桶子再个别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排序)。桶排序是鸽巢排序的一种归纳结果。当要被排序的数组内的数值是均匀分配的时候,桶排序使用线性时间(Θ(n))。但桶排序并不是 比较排序,他不受到 O(n log n) 下限的影响。


- 设置一个定量的数组当作空桶子。
- 寻访序列,并且把项目一个一个放到对应的桶子去。
- 对每个不是空的桶子进行排序。
- 从不是空的桶子里把项目再放回原来的序列中。