B-tree
| EN | CN |
In computer science, a B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree generalizes the binary search tree, allowing for nodes with more than two children.[2] Unlike other self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is well suited for storage systems that read and write relatively large blocks of data, such as discs. It is commonly used in databases and file systems.
According to Knuth’s definition, a B-tree of order m is a tree which satisfies the following properties:
- Every node has at most m children.
- Every non-leaf node (except root) has at least ⌈m/2⌉(means ceil(m / 2)) children.
- The root has at least two children if it is not a leaf node.
- A non-leaf node with k children contains k − 1 keys.
- All leaves are on the bottom level.
Best case and worst case heights
Let h ≥ –1 be the height of the classic B-tree (see Tree (data structure) § Terminology for the tree height definition). Let n ≥ 0 be the number of entries in the tree. Let m be the maximum number of children a node can have. Each node can have at most m−1 keys.
It can be shown (by induction for example) that a B-tree of height h with all its nodes completely filled has \(n = m^(h+1)–1\) entries. Hence, the best case height (i.e. the minimum height) of a B-tree is:
\[h_{min}=\lceil\log_{m}(n+1)\rceil-1\]Let d be the minimum number of children an internal (non-root) node can have.
For an ordinary B-tree, \(d=\left\lceil m/2\right\rceil\)
Comer (1979, p. 127) and Cormen et al. (2001, pp. 383–384) give the worst case height (the maximum height) of a B-tree as
\[h_{max}=\left\lfloor\log_{d}{\frac{n+1}{2}}\right\rfloor\]| Type | Tree (data structure) |
| Invented | 1970[1] |
| Invented by | Rudolf Bayer, Edward M. McCreight |
Time complexity in big O notation
| Algorithm | Average | Worst case |
| Space | O(n) | O(n) |
| Search | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Insert | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| Delete | O(log n) | O(log n) |
Operations on B-Tree
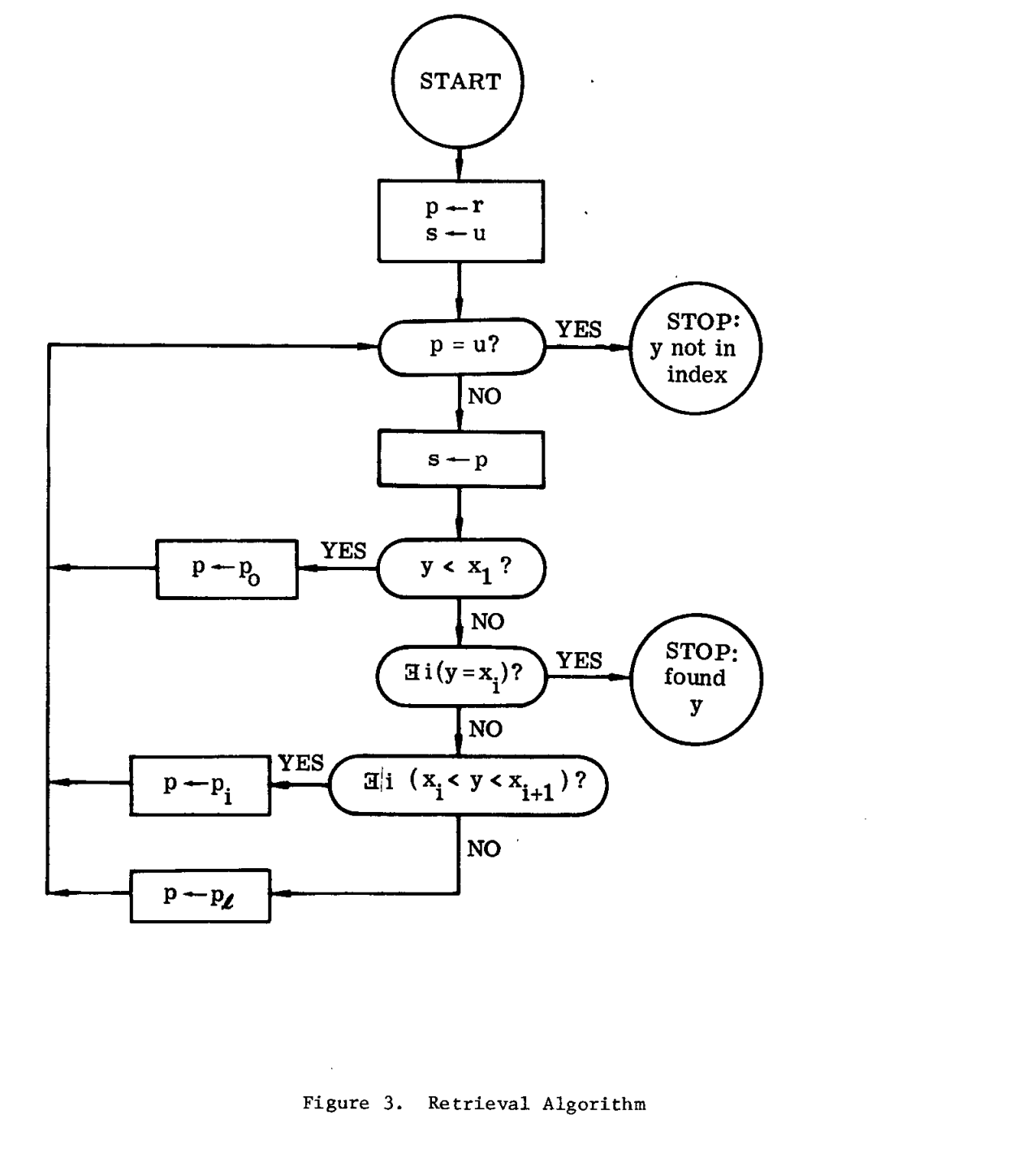
Retrieval
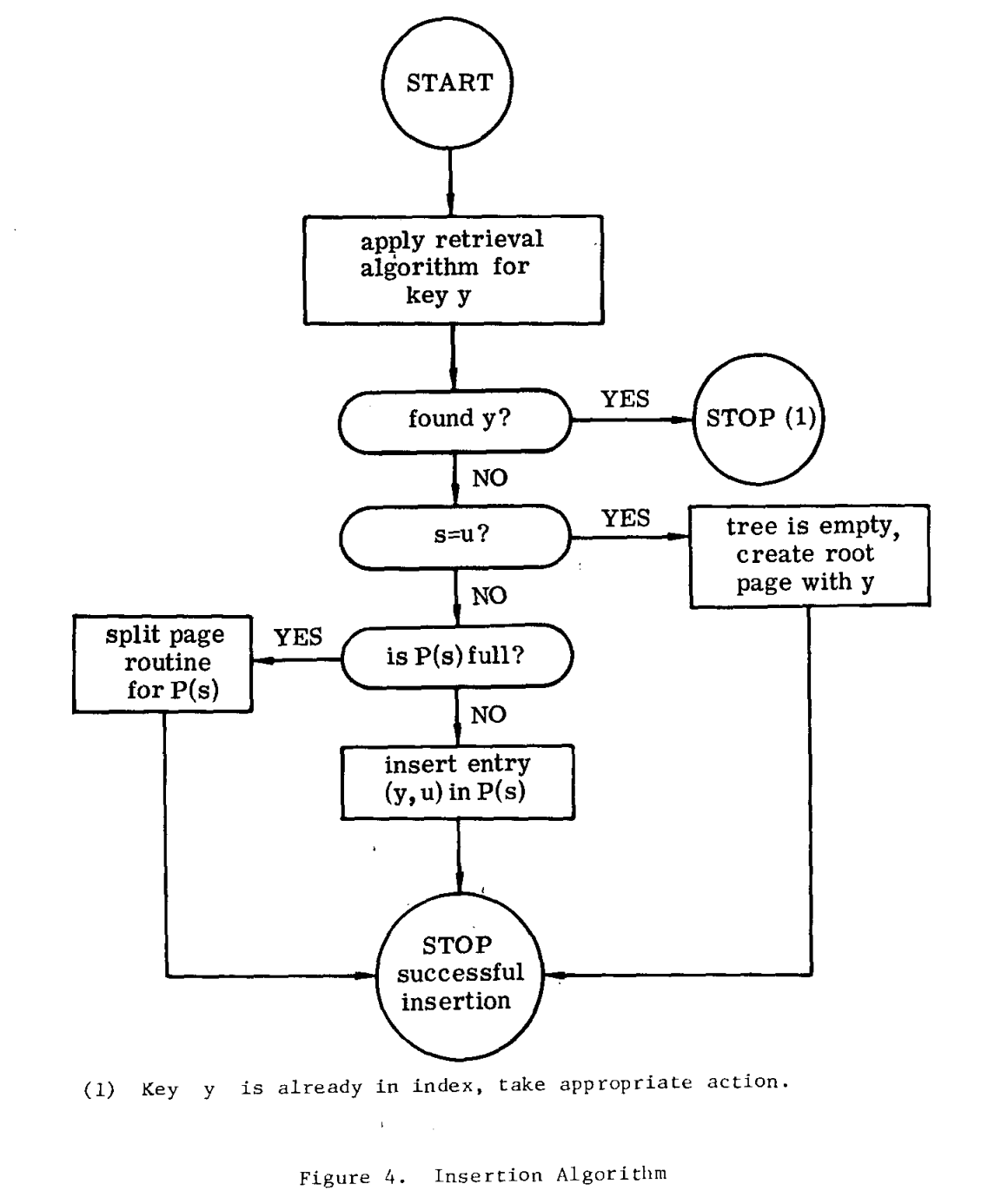
Insertion
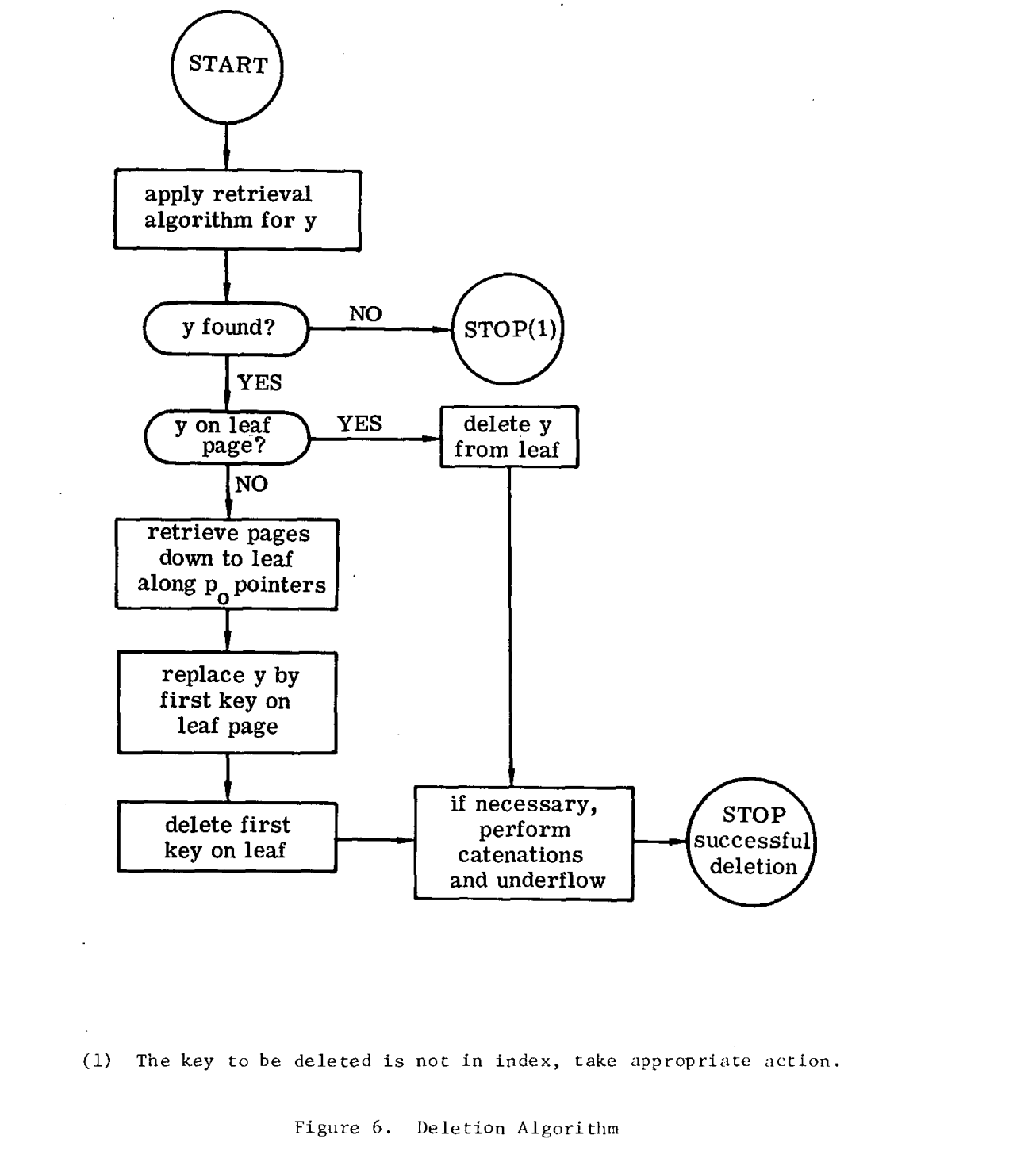
Deletion
Source code
Define BTree.h
Define a C header file of BTree which is included build a NULL BTree, insert, delete, search, travel and destory functions statement.
#ifndef BTree_h
#define BTree_h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define M 4 //the order of B-tree
#define min_keynum (M % 2 ? (M + 1)/2 : M/2)//limit number of key
typedef struct BTNode *BTree, *Position;
typedef int KeyType;
struct BTNode
{
int KeyNum; // number of keys stored in the current node
KeyType Key[M + 1]; // array to hold the KeyNum keys
BTree Child[M + 1]; //array of children pointers
};
/*initialize*/
extern BTree Initialize();
extern BTree Insertion(BTree P, KeyType y);
extern BTree Deletion(BTree P, KeyType y);
extern BTree Destory(BTree P);
extern void DFS(BTree P);
extern void Retrieval(MBTree P, KeyType y);
#endif
BTree.c
Let‘s code these functions
Make a BTree Node
#include "BTree.h"
static KeyType INF = INT_MIN;//-2147483647
/*Make and initialize a btnode */
static BTree MallocBTNode(){
BTree New_BTNode;
int i;
New_BTNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BTNode));
if (New_BTNode == NULL){
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
i = 0;
while(i < M + 1){
New_BTNode->Key[i] = INF;
New_BTNode->Child[i] = NULL;
i++;
}
return New_BTNode;
}
Initialize BTree
extern BTree Initialize(){
BTree P;
if (M < 3){
printf("The multiway tree of order m is less than 3!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/*Root of BTree*/
P = MallocBTNode();
return P;
}
Find Sibling
Finding a sibling node if it’s keys not full then return.
static Position FindSibling(Position Parentnode, int i){
Position Sibling;
int Limit = M;
Sibling = NULL;
if (i == 0){
/*if the sibling of first childnode has no fulled*/
if (Parentnode->Child[1]->KeyNum < Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[1];
}
}
else if (Parentnode->Child[i - 1]-KeyNum < Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[i];
}
/*If the last childnode is not fulled*/
else if (i + 1 < Parentnode->KeyNum && Parentnode->Child[i + 1]->KeyNum < Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[i + 1]
}
return Sibling;
}
Finding Sibling
Finding Sibling which is the KeyNum bigger than [M/2].
static Position FindSibling_M_2(Position Parentnode, int i, int *j){
int Limit = min_keynum;
Position Sibling = NULL;
if (i == 0){
if (Parentnode->Child[1]->KeyNum > Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[1];
*j=1;
}
}else{
if (Parentnode->Child[i - 1]->KeyNum > Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[i - 1];
*j = i - 1;
}
else if (i + 1 < Parentnode->KeyNum && Parentnode->Child[i + 1]->KeyNum > Limit){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[i + 1];
*j = i + 1;
}
}
return Sibling;
}
Insertion Key or Node
| isKey | Judge whether the inserted is Key or Xnode (if Key, insert to Xnode, if Xnode, insert to Parentnode) |
| i | The position of Xnode in Parentnode |
| j | The position of insertion in Xnode |
static Position InsertElement(int isKey, Position Parentnode, Position Xnode, KeyType y, int i, int j){
int k;
if (isKey){
/*insert the y to Xnode*/
k = Xnode->KeyNum - 1;
while (K >= j){
Xnode->Key[k + 1] = X->Key[k];
k--;
}
Xnode->Key[j] = y;
if (Parentnod != NULL){
Parentnode->Key[i] = Xnode->Key[0];
}
Xnode->KeyNum++;
}else{
/*insert the Xnode to Parentnode's Childnode*/
k = Parentnode->KeyNum - 1;
while (k >= i){
Parentnode->Child[k + 1] = Parentnode->Child[k];
Parentnode->Key[k + 1] = Parentnode[k];
k--;
}
Parentnode->Key[i] = Xnode->Key[0];
Parentnode->Child[i] = Xnode;
Parentnode->KeyNum++;
}
return Xnode;
}
Delete Key or Node
| isKey | Judge whether the deleted is Key or Xnode (if Key, delete it in Xnode, if Xnode, delete the Xnode from Parentnode) |
| i | The position of Xnode in Parentnode |
| j | The position of deletions in Xnode |
static Position DeleteElement(int isKey, Position Parentnode, Position Xnode, int i, int j){
int k, Limit;
/*delete the Key which is in jth position in Xnode*/
if (isKey){
Limit = Xnode->KeyNum;
k = j + 1;
while(k < Limit){
Xnode->Key[k - 1] = Xnode->Key[k];
k++;
}
Xnode->Key[Xnode->KeyNum - 1] = INF;
Parentnode->Key[i] = Xnode->Key[0];
Xnode->KeyNum--;
}else{
/*delete the Xnode which is in ith postion in Parentnode*/
Limit = Parentnode->KeyNum;
k = i + 1;
while (k < Limit){
Parentnode->Child[k - 1] = Parentnode->Child[k];
Parentnode->Key[k - 1] = Parentnode->Key[k];
k++;
}
Parentnode->Child[Parentnode->KeyNum - 1] = NULL;
Parentnode->Key[Parentnode->KeyNum - 1] = INF;
Parentnode->KeyNum--;
}
return Xnode;
}
Move Key
| Src | The source node |
| Dst | The destination node |
| n | The number of Keys is moved |
| i | The position of Src/Dst or their children |
/*The Src is silibing of Dst*/
static Position MoveElement(Position Src, Position Dst, Position Parentnode, int i, int n){
KeyType TempKey;
Position Children;
int j, isFront;
isFront = 0;
/*Judge by first Key*/
if (Src->Key[0] < Dst->Key[0]){
isFront = 1;
}
/*if Src in front of Dst */
if (isFront){
if (Src->Child[0] != NULL){
while( j < n){
/*Src->KeyNum will minus one and Children is global variable for these 2 functions*/
Children = Src->Child[Src->KeyNum - 1];
/*Delete Src's last Child*/
DeleteElement(0, Src, Children, Src->KeyNum - 1, INF);
/*Insert the Src's last Child which is not NULL to Dst's first Childnode */
InsertElement(0, Dst, Children, INF, 0, INF);
j++;
}
}else{
/*If Src's children is NULL*/
while (j < n){
/*delete the Src, insert the Src to Dst*/
TempKey = Src->Key[Src->KeyNum - 1];
DeleteElement(1, Parentnode, Src, i, Src->KeyNum - 1);
InsertElement(1, Parentnode, Dst, TempKey, i + 1, 0);
j++;
}
}
Parentnode->Key[i + 1] = Dst->Key[0];
}else{
if (Src->Child[0] != NULL){
while (j < n){
/*Delete the Src's first Childnode, then insert the Src's first Childnode to the rear of Dst's Childnode */
Children = Src->Child[0];
DeleteElement(0, Src, Children, 0, INF);
InsertElement(0, Dst, Children, INF, Dst->KeyNum, INF);
j++;
}
}else{
/*If the Src first chirldnode is NULL, then delete the Src, insert the Scr to Dst*/
while (j < n){
TempKey = Src->Key[0];
DeleteElement(1, Parentnode, Src, i, 0);
InsertElement(1, Parentnode, Dst, TempKey, i - 1, Dst->KeyNum);
j++;
}
}
Parentnode->Key[i] = Src->Key[0];
}
return Parentnode;
}
Split node
static BTree Split(Position Parentnode, Position Xnode, int i){
int j, k , Limit;
Position New_BTNode;
k = 0;
j = Xnode->KeyNum / 2;
Limit = Xnode->KeyNum;
/*Split the half Xnode's Childnodes then insert to New_BTNode's children*/
while (j < Limit){
if (Xnode->Child[0] != NULL){
New_BTNode->Child[k] = Xnode->Child[j];
Xnode->Child[j] = NULL;
}
/*insert the right half Xnode to New_BTNode */
New_BTNode->Key[k] = Xnode->Key[j];
Xnode->Key[j] = INF;
New_BTNode->KeyNum++;
Xnode->KeyNum--;
j++;
k++;
}
if (Parentnode != NULL){
/*insert the NewBTNode to Parentnode's Childnode*/
InsertElement(0, Parentnode, New_BTNode, INF, i + 1, INF);
}else{
/*if Parentnode is None, create new parentnode, then insert Xnode and New_BTNode to new Parentnode*/
P = MallocBTNode();
InsertElement(0, P, Xnode, INF, 0, INF);
InsertElement(0, P, New_BTNode, INF, 1, INF);
return P;
}
return Xnode;
}
Merge Node
Snode is Sibling of Xnode
Xnode only has one Key, Snode has more than or equal to [M/2] Keys.
static Position Merge(Position Parentnode, Position Xnode, Position Snode, int i){
int Limit;
/*Move one Key from Snode to Xnode*/
if (Snode->KeyNum > min_keynum){
MoveElement(Snode, Xnode, Parentnode, i, 1);
}else{
/*Merge Xnode and Snode*/
Limit = Xnode->KeyNum;
MoveElement(Xnode, Snode, Parentnode, i, Limit);
DeleteElement(0, Parentnode, Xnode, i, INF);
free(Xnode);
Xnode = NULL;
}
return Parentnode;
}
RecursiveInsert node
static BTree RecursiveInsert(BTree T, KeyType y, int i, BTree Parentnode){
int j, Limit;
Position Sibling;
/*find the NULL childnode*/
j = 0;
while (j < T->KeyNum && y >= T->Key[j]){
if (y == T->Key[j]){
return T;
}
j++;
}
/*back one step*/
if (j != 0 && T->Child[0] != NULL){
j--;
}
/*if the T has no first child, insert the y to T*/
if (T->child[0] == NULL){
T = InsertElement(1, Parentnode, T, y, i, j):
}else{
/*insert y to the T's childnodes*/
T->Child[j] = RecursiveInsert(T->Child[j], y, j, T);
}
/*Adjust the T if the Keys is fullest*/
Limit = M;
if (T->KeyNum > Limit){
/*if the T is the root of BTree, create a new root then split the T */
if (Parentnode == NULL){
T = Split(Parentnode, T, i);
}else{
/*Finding the Parentnode's childnodes if they have a sibling node its keys not full then return the childnode*/
Sibling = FindSibling(Parentnode, i);
if (Sibling != NULL){
/*Move one Key or Childnode from T to Sibling*/
MoveElement(T, Sibling, Parentnode, i, 1);
}else{
T = Split(Parentnode, T, i);
}
}
}
if (Parentnode != NULL){
Parentnode->Key[i] = T->Key[0]
}
return T;
}
extern BTree Insertion(BTree P, KeyType y){
return RecursiveInsert(P, y, 0, NULL);
}
RecursiveDelete Key or Node
static BTree RecursiveDelete(BTree T, KeyType y, int i, BTree Parentnode){
int i, Adjust;
Position Sibling, Tmp;
Sibling = NULL;
/*Finding the positon where to delete*/
j = 0;
while (j < T->KeyNum && y >= T->Key[j]){
if (y == T->Key[j]){
break;
}
j++;
}
if (T->Child[0] == NULL){
/*if not found in T*/
if (y != T->Key[j] || j == T->KeyNum){
return T;
}
}else{
/*back one step then look up in T's childnodes*/
if (j == T->KeyNum || y < T->Key[j]){
j--;
}
}
/*If found, then delete the Key in the ith position of T*/
if (T->Child[0] == NULL){
T = DeleteElement(1, Parentnode, T, i, j);
}else{
/*Finding the y in the T's childnodes*/
T->Child[j] = RecursiveDelete(T->Child[j], y, j, T);
}
Adjust = 0;
if (Parentnode == NULL && T->Child[0] != NULL && T->KeyNum < 2){
Adjust = 1;
}
else if (Parentnode != NULL && T->Child[0] != NULL && T->KeyNum < min_keynum){
Adjust = 1;
}
else if (Parentnode != NULL && T->Child[0] == NULL && T->KeyNum < min_keynum){
Adjust = 1;
}
if (Adjust){
/*If it is root*/
if (Parentnode == NULL){
/*if the root has childnode and its number of keys is less than 2, delete the root, move up the first childnode of T*/
if (T->Child[0] != NULL && T->KeyNum < 2){
Tmp = T;
T = T->Child[0];
free(Tmp);
return T;
}
}else{
/*Finding the sibling node its number of keys is more than M/2*/
Sibling = FindSibling_M_2(Parentnode, i, &j);
/*Move the one Key of Sibling or the whole Sibling to T if its key bigger than T's */
if (Sibling != NULL){
MoveElement(Sibling, T, Parentnode, j, 1)
}else{
if (i == 0){
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[1];
}else{
Sibling = Parentnode->Child[i - 1];
}
/*Merge Sibling and T or move one Key from Sibling to T*/
Parentnode = Merge(Parentnode, T, Sibling, i);
T = Parentnode->Child[i];
}
}
}
return T;
}
extern BTree Deletion(BTree P, KeyType y){
return RecursiveDelete(P, y, 0, NULL);
}
Destory BTree
extern BTree Destory(BTree P){
int i,j;
if (P != NULL){
i = 0;
while (i < P->KeyNum + 1){
Destory(P->Child[i]);
i++;
}
free(P);
P = NULL;
}
return P;
}
Travel BTree
static void RecursiveTravel(BTree T, int Level){
int i;
if (T != NULL){
for(i = 0; i < Level;i++){
printf(" ");
}
printf("[Level:%d]-->(",Level);
if (T->Child[0] == NULL){
i = 0;
}else{
i = 1;
}
while (i < T->KeyNum){
printf("%d:", T->Key[i++]);
}
printf(")\n");
Level++;
i = 0;
while (i <= T->KeyNum){
RecursiveTravel(T->Child[i], Level);
i++;
}
}
}
extern void DFS(BTree P){
RecursiveTravel(P, 0);
}
Search Node
extern int Search(MBTree P, KeyType y, int Level, int found){
int i = 0;
if (P != NULL){
while (i <= P->KeyNum){
if (y == P->Key[i]){
printf("We found the key:%d in %dth level\n", y, Level);
found = 1;
return found;
}
i++;
}
if (found == 0){
i = 0;
Level++;
while (i <= P->KeyNum){
found = Search(P->Children[i], y, Level, found);
i++;
}
}
}
return found;
}
extern void Retrieval(MBTree T, KeyType y){
int found = Search(T, y, 0, 0);
if (found == 0){
printf("No found\n");
}
}
Main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "BTree.h"
int main(void){
BTree P;
P = Initialize();
clock_t c1 = clock();
int i = 100;
while (i > 0){
P = Insertion(P, i--);
}
clock_t c2 = clock();
unsigned long t = (c2 - c1)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
DFS(P);
Retrieval(T, 100); //return "We found the key:100 in 3th level"
Retrieval(T, 101); //return No found
Destory(P);
printf("\nTotal used time is %lus\n", t);
return 0;
}
Reference
B树
在计算机科学中,B树(英语:B-tree)是一种自平衡的树,能够保持数据有序。这种数据结构能够让查找数据、顺序访问、插入数据及删除的动作,都在对数时间内完成。B树,概括来说是一个一般化的二叉查找树(binary search tree)一个节点可以拥有2个以上的子节点。与自平衡二叉查找树不同,B树适用于读写相对大的数据块的存储系统,例如磁盘。B树减少定位记录时所经历的中间过程,从而加快存取速度。B树这种数据结构可以用来描述外部存储。这种数据结构常被应用在数据库和文件系统的实现上。
B树优点
- 保持键值有序,以顺序遍历
- 使用层次化的索引来最小化磁盘读取
- 使用不完全填充的块来加速插入和删除
- 通过优雅的遍历算法来保持索引平衡
- 另外,B树通过保证内部节点至少半满来最小化空间浪费。一棵B树可以处理任意数目的插入和删除。
B树缺点
除非完全重建数据库,否则无法改变键值的最大长度。这使得许多数据库系统将人名截断到70字符之内。
搜索

插入

删除

源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
/* B树结点结构 */
typedef struct _btree_node_t
{
int num; /* 关键字个数 */
int *key; /* 关键字:所占空间为(max+1) - 多出来的1个空间用于交换空间使用 */
struct _btree_node_t **child; /* 子结点:所占空间为(max+2)- 多出来的1个空间用于交换空间使用 */
struct _btree_node_t *parent; /* 父结点 */
}btree_node_t;
/* B树结构 */
typedef struct
{
int max; /* 单个结点最大关键字个数 - 阶m=max+1 */
int min; /* 单个结点最小关键字个数 */
int sidx; /* 分裂索引 = (max+1)/2 */
btree_node_t *root; /* B树根结点地址 */
}btree_t;
/******************************************************************************
**函数名称: btree_creat
**功 能: 创建B树
**输入参数:
** _btree: B树
** m: 阶 - 取值范围m>=3
**输出参数: NULL
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失败
**实现描述:
**注意事项: 参数max的值不能小于2.
******************************************************************************/
int btree_creat(btree_t **_btree, int m)
{
btree_t *btree = NULL;
if(m < 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Parameter 'max' must geater than 2.\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
btree = (btree_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(btree_t));
if(NULL == btree) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
btree->max= m - 1;
btree->min = m/2;
if(0 != m%2) {
btree->min++;
}
btree->min--;
btree->sidx = m/2;
btree->root = NULL; /* 空树 */
*_btree = btree;
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
**函数名称: btree_creat_node
**功 能: 新建结点
**输入参数:
** btree: B树
**输出参数: NONE
**返 回: 节点地址
******************************************************************************/
static btree_node_t *btree_creat_node(btree_t *btree)
{
btree_node_t *node = NULL;
node = (btree_node_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(btree_node_t));
if(NULL == node) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
node->num = 0;
/* More than (max) is for move */
node->key = (int *)calloc(btree->max+1, sizeof(int));
if(NULL == node->key) {
free(node), node=NULL;
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
/* More than (max+1) is for move */
node->child = (btree_node_t **)calloc(btree->max+2, sizeof(btree_node_t *));
if(NULL == node->child) {
free(node->key);
free(node), node=NULL;
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
return node;
}
/******************************************************************************
**函数名称: btree_split
**功 能: 结点分裂处理
**输入参数:
** btree: B树
** node: 需要被分裂处理的结点
**输出参数: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失败
******************************************************************************/
static int btree_split(btree_t *btree, btree_node_t *node)
{
int idx = 0, total = 0, sidx = btree->sidx;
btree_node_t *parent = NULL, *node2 = NULL;
while(node->num > btree->max) {
/* Split node */
total = node->num;
node2 = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == node2) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create node failed!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
/* Copy data */
memcpy(node2->key, node->key + sidx + 1, (total-sidx-1) * sizeof(int)); /*把node的中位数位置右边的关键字复制到node2*/
memcpy(node2->child, node->child+sidx+1, (total-sidx) * sizeof(btree_node_t *));/*把node子节点中位数位置右边的关键字复制给node2的子节点*/
node2->num = (total - sidx - 1);
node2->parent = node->parent;
node->num = sidx;
/* Insert into parent */
parent = node->parent;
if(NULL == parent){
/* Split root node 更新根节点*/
parent = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == parent) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create root failed!", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
btree->root = parent;
parent->child[0] = node;
node->parent = parent;
node2->parent = parent;
parent->key[0] = node->key[sidx];/*node节点的中位数作为新的根节点*/
parent->child[1] = node2;
parent->num++;
printf("分裂根节点: %d\n", parent->key[0]);
}
else {
/* Insert into parent node */
for(idx=parent->num; idx>0; idx--) {
if(node->key[sidx] < parent->key[idx-1]) {
parent->key[idx] = parent->key[idx-1]; /*大于要插入节点值的父节点key向后移动*/
parent->child[idx+1] = parent->child[idx]; /*指向儿子节点的指针向后移动*/
continue;
}
break;
}
/*相等*/
parent->key[idx] = node->key[sidx];
parent->child[idx+1] = node2;
node2->parent = parent;
parent->num++;
printf("插入父节点:parent->key[%d]= %d \n", idx, parent->key[idx]);
}
memset(node->key+sidx, 0, (total - sidx) * sizeof(int));
memset(node->child+sidx+1, 0, (total - sidx) * sizeof(btree_node_t *));
/* Change node2's child->parent */
for(idx=0; idx<=node2->num; idx++) {
if(NULL != node2->child[idx]) {
node2->child[idx]->parent = node2;
}
}
node = parent;
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
**函数名称: _btree_insert
**功 能: 插入关键字到指定结点
**输入参数:
** btree: B树
** node: 指定结点
** key: 被插入的关键字
** idx: 指定位置
**输出参数: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失败
**实现描述:
**注意事项:
******************************************************************************/
static int _btree_insert(btree_t *btree, btree_node_t *node, int key, int idx)
{
int i = 0;
/* 1. 移动关键字:首先在最底层的某个非终端结点上插入一个关键字,因此该结点无孩子结点,故不涉及孩子指针的移动操作 */
for(i=node->num; i>idx; i--) {
node->key[i] = node->key[i-1];
}
printf("node->key[%d]=%d\n",idx, key );
node->key[idx] = key; /* 插入 */
node->num++;
/* 2. 分裂处理 */
if(node->num > btree->max) {
return btree_split(btree, node);
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
**函数名称: btree_insert
**功 能: 插入关键字(对外接口)
**输入参数:
** btree: B树
** key: 被插入的关键字
**输出参数: NULL
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失败
**实现描述:
**注意事项:
******************************************************************************/
int btree_insert(btree_t *btree, int key)
{
int idx = 0;
btree_node_t *node = btree->root;
/* 1. 构建第一个结点 */
if(NULL == node) {
node = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == node) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create node failed!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
node->num = 1;
node->key[0] = key;
node->parent = NULL;
btree->root = node;
printf("BTree's root: %d\n", node->key[0]);
return 0;
}
/* 2. 查找插入位置:在此当然也可以采用二分查找算法,有兴趣的可以自己去优化 */
while(NULL != node) {
for(idx=0; idx<node->num; idx++) {
/*防止重复插入*/
if(key == node->key[idx]) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] The node is exist!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
else if(key < node->key[idx]) {
break;
}
}
if(NULL != node->child[idx]) {
node = node->child[idx];
}
else {
break;
}
}
/* 3. 执行插入操作 */
return _btree_insert(btree, node, key, idx);
}
static void RecursiveTravel(btree_node_t *root, int Level){
int i;
if (root != NULL){
i = 0;
while (i < 3/2) {
RecursiveTravel(root->child[i], Level);
i++;
}
for(int j = 0; j < Level; j++){
printf(" ");
}
i = 0;
while (i < root->num){
printf("%d ",root->key[i]);
i++;
}
printf("\n");
Level++;
i = 3/2;
while (i <= 3) {
RecursiveTravel(root->child[i], Level);
i++;
}
}
return;
}
//中序遍历
void Travel(btree_t *btree){
RecursiveTravel(btree->root, 0);
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int n[6] = {2,3,4,5,5,6};
btree_t *btree;
int m = 4;
btree_creat(&btree, m);
int i = 10;
while (i > 0){
btree_insert(btree, i);
i--;
}
Travel(btree);
int i = 1;
if(i){
printf("1\n");
}else{
printf("2\n");
}
return 0;
}