作者简介
作者团队来自 Google Research
1. Ashish Vaswani
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Ashish Vaswani 主要研究自然语言处理(NLP)、深度学习和神经网络架构,尤其是与序列建模、机器翻译和自注意力机制(Self-Attention)相关的工作。
- 贡献:《Attention Is All You Need》论文的第一作者,他是 Transformer 架构的主要贡献者之一。该论文介绍了 Transformer 模型,彻底改变了深度学习在自然语言处理任务中的应用。
2. Noam Shazeer
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Noam Shazeer 主要专注于深度学习和自然语言处理领域,尤其是在神经网络架构和模型优化方面的工作。
- 贡献:Shazeer 是 Transformer 的核心设计者之一,也是论文中许多重要思想的推动者。他在 Google 的机器翻译团队工作,并且参与了 Google 的开源库 TensorFlow 和其他深度学习工具的开发。
3. Niki Parmar
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Niki Parmar 的研究兴趣包括深度学习和自然语言处理,特别是在处理复杂序列数据和推理问题方面。
- 贡献:在《Attention Is All You Need》论文中,Parmar 贡献了模型的设计和实验工作,尤其是通过自注意力机制改进了传统的序列建模方法。
4. Jakob Uszkoreit
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Jakob Uszkoreit 的研究领域涉及自然语言处理、深度学习以及语义解析。
- 贡献:Uszkoreit 在 Transformer 模型的设计和优化方面做出了贡献,尤其在模型如何处理长序列的相关性和计算效率方面。
5. Llion Jones
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Llion Jones 主要关注深度学习、计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域。
- 贡献:他在 Transformer 模型的开发过程中,负责了部分关键的算法优化和模型实现。
6. Aidan N. Gomez
- 职位:研究员,曾在 University of Toronto 和 Google Research 工作。
- 研究领域:Aidan Gomez 主要研究深度学习和神经网络,尤其是 Transformer 架构及其改进方法。
- 贡献:Gomez 在 Transformer 的设计和实验验证中扮演了关键角色,尤其是在如何提高模型的效率和性能方面。
7. Lukasz Kaiser
- 职位:Google Research的研究科学家。
- 研究领域:Lukasz Kaiser 的研究专注于深度学习、自然语言处理以及强化学习等领域。
- 贡献:Kaiser 是 Transformer 架构的共同设计者之一,并且在优化算法和效率提升方面做出了贡献。
8. Illia Polosukhin
- 职位:深度学习工程师,曾在 Google Research 工作。
- 研究领域:Illia Polosukhin 主要研究深度学习和自然语言处理,尤其关注如何改进神经网络模型的训练和应用。
- 贡献:Polosukhin 参与了 Transformer 架构的设计和实现,并在论文中对模型的性能和创新提出了重要的贡献。
定义
它是一种深度学习架构, 由编码器和解码器组成, 利用“多头自注意力机制”, 应用于自然语言处理,计算机视觉.
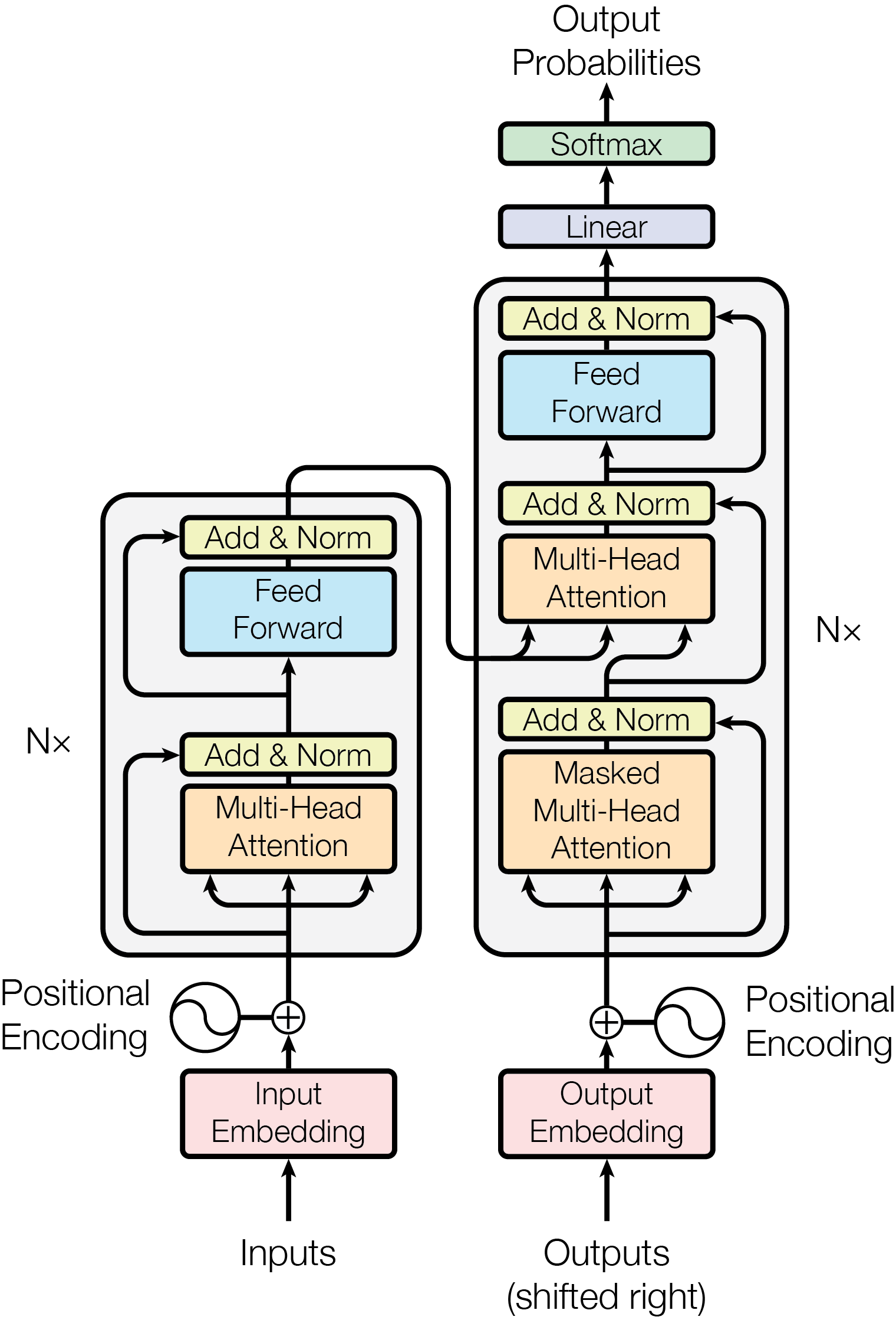
shifted right(右移)
将目标序列整体向右移动一个位置,
解码器的输入(tgt): [“
而目标输出(tgt_y): [“I”, “love”, “NLP”, “
目的:对齐t-1时刻的token(例如:”
输入嵌入(Input Embedding)
将离散的输入的token(如单词、子词、字符等)转换为连续的向量表示. 其中weight如未提供,则从标准正太分布中随机采样出一个(num_embeddings, embedding_dim) 的张量,num_embeddings=词汇表的大小,embedding_dim=每个嵌入向量的维度。
为什么不用ASCII码或者One-hot编码表示而是Word embeddings
| 特性 | One-Hot 编码 | Word Embedding |
|---|---|---|
| 维度 | 维度等于词汇表的大小 ( V ),例如,如果词汇表有 10,000 个词,向量的维度就是 10,000。 | 维度可以较小,通常在 50 到 300 之间。 |
| 稀疏性 | 非常稀疏,除了表示当前词的那个位置为 1,其他位置都是 0。 | 密集向量,所有值通常都为非零实数。 |
| 词之间的关系 | 词与词之间没有任何语义关系,每个词的表示都是独立的。 | 通过训练,词嵌入能捕捉到词与词之间的语义关系。 |
| 存储需求 | 由于维度高,存储需求大,尤其是词汇表很大的时候。 | 存储需求较低,因为嵌入向量维度较小。 |
| 训练时间 | 每个词需要占用整个向量空间,计算和存储都很耗时。 | 训练过程更高效,能够通过神经网络学习到有意义的嵌入向量。 |
| 表示能力 | 不能表示词之间的相似性或关系,只能标识一个词。 | 能够通过距离和角度来表示词之间的相似性和关系。 |
| 泛化能力 | 对于新词,无法直接表示,只能进行词汇表的扩展。 | 可以通过“未见过的词”的近似嵌入进行泛化。 |
| 应用 | 适合简单的分类任务或只有少量词汇的任务。 | 适合处理更复杂的任务,如语言建模、翻译、情感分析等。 |
位置编码(Positional Encoding)
由于 Transformer 不依赖 RNN 或 CNN 的顺序结构,使用位置编码为输入向量添加位置信息,以区分序列中各位置。
\(PE(pos, k)=\begin{cases} sin(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{k}{d}} } ) &\text{if k = 2i} \\ cos(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{k}{d}} } ) &\text{if k = 2i +1} \end{cases}\)
- pos表示token位置
- i表示维度
为什么使用三角函数
- 限定范围在[-1, 1]
- 连续性
- 相对位置
为什么要分为sin和cos
- tensor2tensor 的作者(Ashish Vaswani 和 Noam Shazeer 都是 “Attention Is All You Need” 的作者,同时也参与了 Tensor2Tensor 项目的开发。)解释奇偶区分可以通过全连接层帮助重排坐标,所以可以直接简单地分为两段(前 256 维使用 sin,后 256 维使用 cos)
I think this does not matter, since there is a fully connected layer after the encoding is added(and before) and it can permute the coordinates
- 数学性质,和差化积公式
为什么是10000
- 实验得出
有没有更好的位置编码方式
| 位置编码 | 是否可学习 | 是否支持长序列 | 计算开销 | 适用任务 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三角函数位置编码 | ❌ 否 | ✅ 是 | 低 | Transformer 基础模型 |
| 可学习位置编码Learnable | ✅ 是 | ❌ 否 | 低 | 语言建模(GPT, BERT) |
| 相对位置编码Relative | ✅ 是 | ✅ 是 | 低 | 机器翻译,文本生成 |
| 旋转式位置编码RoPE | ✅ 是 | ✅ 是 | 低 | GPT, LLaMA |
| ALiBi | ✅ 是 | ✅ 是 | 极低 | 超长文本任务 |
编码器(Encoder)
由6层相同的层构成, 每层有2个子层, 1层为多头自注意力层, 1层为position-wise全连接前馈网络层(FFN), 其中position-wise是一种处理方式,表示不考虑元素的相对位置而采取相同的操作. 通过残差连接包围两个子层 然后连接层归一化(Layer Normalization), 输出维度为\(d_{model} = 512\)
解码器(Decoder)
由6个相同层构成, 每层有3个子层, 1层为掩码多头自注意力层(Masked Multi-heads self-attetion mechanism), 1层为position-wise全连接前馈网络层(FFN), 1层是多头自注意力层(它接入编码器的输出). 通过残差连接包围两个子层 然后连接层归一化(Layer Normalization), 输出维度为\(d_{model} = 512\)
Mask的主要目的是防作弊, 防止后位置影响前位置
多头自注意力机制(Multi-heads Self Attention)

缩放点积注意力(Scaled Dot-Product Attention)
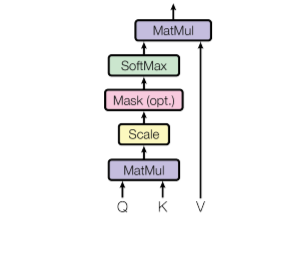
为什么要乘以\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d_k}}\)
在维度\(d_k\)较大时,不使用缩放因子的计算会使得内积值变得过大,导致 softmax 的输出趋向于 0 或 1,进而使得注意力机制的权重分布过于极端,影响模型的表现
为什么乘以\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d_k}}\)而不是\(\frac{1}{d_k}\)
假设组成Q,K的随机变量是独立的且服从均值为0,方差为1的分布, 则
\[z^2 = \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{i = 1}^{d_k}\sum_{j = 1}^{d_k}(q_ik_j - \mu)^2\] \[\begin{align} 其中, \mu &= E(q_i,k_j) = \frac{1}{d_k^2} \sum_{i = 1}^{d_k}\sum_{j = 1}^{d_k}(q_ik_j)\\ 并且, E(q_i) &= \frac{1}{d_k}\sum_{i=1}^{d_k}q_i=0\\ E(k_j) &= \frac{1}{d_k}\sum_{j=1}^{d_k}k_j=0\\ 所以, E(q_i,k_j) &=E(q_i)E(k_j) = 0\\ 此外, V(q_i) &= \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{i=1}^{d_k}(q_i-E(q_i))^2 = \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{i=1}^{d_k}q_i^2=1\\ V(k_j) &= \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{j=1}^{d_k}(k_j-E(k_j))^2 = \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{j=1}^{d_k}k_j^2=1\\ 所以, z^2 &= \frac{1}{d_k} \sum_{i = 1}^{d_k}\sum_{j = 1}^{d_k}(q_ik_j)^2=V(q_i)V(k_j)d_k=d_k\Rightarrow std(z) = \sqrt{d_k} \end{align}\]多头注意力(Multi-Head Attention)
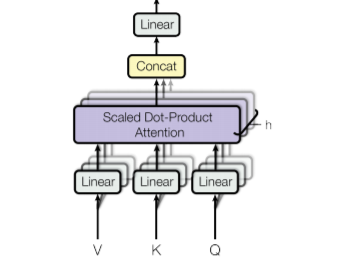
\(\begin{matrix} MultiHead(Q, K, V) = Concat(head_1, head_2,...,head_h)W^O \\\text{Where }head_i = Attention(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V) \end{matrix}\)
- h = 8
- \(d_k = d_v=d_{model}/h =\)64
- \(W^O\)表示输出权重矩阵,\(\in \mathbb{R} ^{hd_v\times d_{model}}\)
- \(W_i^Q\) 是 第 i 个头注意力的查询(Query)权重矩阵,\(\in \mathbb{R} ^{d_k\times d_{model}}\)
- \(W_i^K\) 是第 i 个头注意力的键(Key)权重矩阵,\(\in \mathbb{R} ^{d_k\times d_{model}}\)
- \(W_i^V\) 是第 i 个头注意力的值(Value)权重矩阵,\(\in \mathbb{R} ^{d_v\times d_{model}}\)
为什么MHA不能是任意个,而是h=8(即16个多头注意力)
显然并不是一定要16个MHA, 根据Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One?中通过实验发现,即使在训练时使用了多个注意力头,在测试时很多头是可以被移除而不显著影响模型性能的。多头注意力可能并不是每个头都必不可少,有些可能是冗余的。
在前面的实验中,研究表明某些注意力头比其他头更重要。为了深入了解这一现象,研究团队在训练的不同阶段进行了逐步剪枝实验,以观察注意力头重要性在训练过程中的变化。
1. 研究方法
- 选用 IWSLT 2014 德英翻译数据集 训练一个小型 Transformer(6 层,8 头/层)。
- 在每个训练周期(epoch)进行剪枝实验,测试剪枝后模型性能下降的程度。
- 记录 BLEU 分数的变化,并使用对数尺度绘制不同训练阶段的趋势。
2. 主要发现
- 训练初期(epoch 1-2):
- 头的重要性分布较均匀,即所有注意力头对模型的贡献大致相同。
- 剪枝的影响呈 线性下降,表明早期训练阶段模型对所有头的依赖较为均匀。
- 训练中后期(epoch 10 及以后):
- 出现了一批冗余的注意力头,这些头被剪枝后仍能保持 85%-90% 的原始 BLEU 分数。
- 最多可剪掉 40% 的注意力头,而不会显著降低翻译质量。
- 注意力头的重要性在训练过程中逐渐分化:
- 早期(epoch 1-2):所有头贡献相似,无明显主次。
- 中期(epoch 10+):模型逐渐学习到最重要的头,并开始依赖它们,而其他头变得可有可无。
3. 关联信息理论
研究结果与 Shwartz-Ziv 和 Tishby(2017) 关于神经网络训练的两阶段理论相吻合:
- 阶段 1:经验风险最小化(Empirical Risk Minimization)
- 目标:最大化输入与标签的互信息,模型学习尽可能多的信息。
- 早期训练阶段,所有注意力头贡献接近,尚未区分出最重要的头。
- 阶段 2:压缩阶段(Compression Phase)
- 目标:最小化输入信息冗余,模型开始仅保留最有效的信息通道。
- 训练后期,少数头变得更重要,而其他头逐渐被模型忽略,成为冗余头。
掩码多头注意力(Masked Multi-Head Attention)
防作弊规则,只能看到过去与现在的向量
| Attention Pattern | \(( \vec{K_1} )\) | \(( \vec{K_2} )\) | \(( \vec{K_3} )\) | \(( \vec{K_4} )\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(( \vec{Q_1} )\) | 0.2 | -inf | -inf | -inf |
| \(( \vec{Q_2} )\) | 0.3 | 0.1 | -inf | -inf |
| \(( \vec{Q_3} )\) | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | -inf |
| \(( \vec{Q_4} )\) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.1 |
逐位置前馈网络(Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks)
\[FFN(x)= max(0,xW_1+ b_1)W_2 + b_2\]先投影到\(d_{ff}=2048\)维度的张量空间然后在缩放回\(d_{model}=512\)
为什么是\(d_{ff}\)等于2048
一个经过实验验证的经验数值, 在性能、计算效率和模型复杂度之间取得了良好的平衡.
优化器(Optimizer)
Adam: β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.98 and ϵ = 1e−9
\[\begin{matrix} \eta = \frac{min(\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{\text{step_num}} }, \frac{\text{step_num}}{\sqrt[]{\text{warmup_steps} ^3} } )}{\sqrt[]{d_{model}} } \\ \text{where warmup_steps} = 4000 \end{matrix}\]- 预热阶段:从0到4000步,学习率逐渐增大。
- 后期阶段:从4000步之后,学习率逐渐减小。
正则化(Regularization)
残差随机失活(Residual Dropout)
\[y=F(x)+Dropout(x)\]残差连接的加和部分也可能被随机丢弃. 使用\(P_{drop} = 0.1\), 应用与每个输出的子层之后,dropout 会随机丢弃输出中的一部分神经元,然后,这个被丢弃的输出将会与子层输入相加,输入到正则化层和每个子层。累加嵌入层和位置编码也应用了dropout
dropout的流程
如果0<p<1:
- 根据1-p使用伯努利分布生成器生成一张0,1的二值矩阵, 0表示丢弃:\(P(X=x) = p^x (1-p)^{1-x}\)
- 生成的矩阵先乘以1/(1-p),保持期望不变,再点乘原矩阵
- 输出
软化目标标签(Label Smoothing)
目的:防止模型过于自信地做出预测,并通过减少模型对错误标签的过度拟合,从而提高泛化能力.
平滑过程如下:
- 将正确标签的概率值从 1 调整为 1−ϵ(例如,0.9)。
- 将剩余的概率(ϵ)均匀分配给所有其他类别(例如,0.05)。
例如:
- 类别 1:[0.9, 0.05, 0.05]
- 类别 2:[0.05, 0.9, 0.05]
- 类别 3:[0.05, 0.05, 0.9]
适用场景:
- 大规模分类问题,尤其是当存在过拟合或泛化问题时。
- 类别不平衡,防止模型对少数类过度拟合。
- 避免过度自信,减少训练过程中模型输出的极端概率。
- 生成任务(如机器翻译和语言建模),让模型产生多样化的输出。
- 标签噪声的存在时,减少噪声对训练的影响。
- 多任务学习,提高不同任务之间的信息共享。
解决什么问题
- 克服了 RNN 的顺序依赖和并行化困难
- 增强长序列依赖的建模能力
- 减少计算路径,提高训练效率
- 提供更灵活的上下文建模能力
- 统一了模型架构,简化设计和扩展
优点
| 特点/优点 | Transformer | RNN | LSTM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 模型架构 | 基于自注意力机制(Self-Attention) | 基于递归神经网络,逐步处理序列数据 | 基于长短时记忆单元(LSTM)解决 RNN 的长期依赖问题 |
| 并行处理 | 可以并行处理整个序列,适合大规模数据训练 | 逐步处理,无法并行处理,训练速度慢 | 逐步处理,虽然有记忆单元,但仍无法完全并行 |
| 长距离依赖 | 通过自注意力机制处理长距离依赖,能直接关注序列中任意位置的相关性 | 难以捕捉长距离依赖,梯度消失或爆炸问题 | 能较好处理长距离依赖,但仍然受限于网络的深度与复杂性 |
| 计算效率 | 使用自注意力机制计算效率高,可以并行化计算 | 计算依赖于序列的长度,计算效率低 | 计算比 RNN 更复杂,性能受限于门控机制和时间步长的数量 |
| 训练时间 | 因为可以并行计算,所以训练速度较快 | 随着序列长度的增加,训练时间增长较快 | 虽然比 RNN 更快,但由于复杂的计算,仍然较慢 |
| 上下文建模 | 通过自注意力机制,能够捕捉全局上下文信息 | 只能按顺序逐步处理,不能同时处理全局上下文信息 | 类似于 RNN,但有更强的记忆能力,仍然是逐步处理 |
| 模型可扩展性 | 高度可扩展,适合大规模数据和更深层次的网络结构 | 随着网络深度增加,计算变得更加困难,容易出现梯度消失问题 | 在深层次结构中表现更好,但仍然存在梯度消失的问题 |
| 模型复杂度 | 基于全连接的自注意力层,计算量大,参数多 | 结构简单,参数少,但无法处理长时间序列 | 比 RNN 更复杂,结构复杂,门控单元使得其计算成本较高 |
| 适用场景 | 适用于机器翻译、文本生成、图像处理等需要捕捉长距离依赖的任务 | 适用于序列预测,但在长序列任务上表现较差 | 适用于序列任务,如时间序列预测、语音识别等 |
| 模型表现 | 在各种 NLP 任务上表现优异,尤其是在翻译、文本生成等任务上 | 在处理短序列时表现较好,长序列的处理存在困难 | 对长序列有较好表现,但仍然逊色于 Transformer 模型的表现 |
缺点
- 计算资源消耗高:Transformer 的自注意力机制需要对每对输入元素计算相似度,计算复杂度为 (O(n^2)),随着序列长度的增加,计算和内存需求急剧上升。这使得 Transformer 在处理长序列时非常耗费计算资源。
- 对长序列处理的限制:尽管 Transformer 可以捕捉全局依赖,但其计算复杂度随着序列长度增加而急剧增加。在序列非常长时,计算和内存消耗成为瓶颈。
- 训练时间长:特别是在多层堆叠时,Transformer 的训练时间较长。尽管可以并行处理序列,但每个位置之间的相似度计算仍然需要时间。
- 对小数据集的适应性差:Transformer 模型需要大量的数据才能达到良好的性能。对于小数据集,Transformer 容易过拟合,训练效果不理想。
数据集
训练硬件和时间
- 8 个 NVIDIA P100 GPU
- 3.5 天
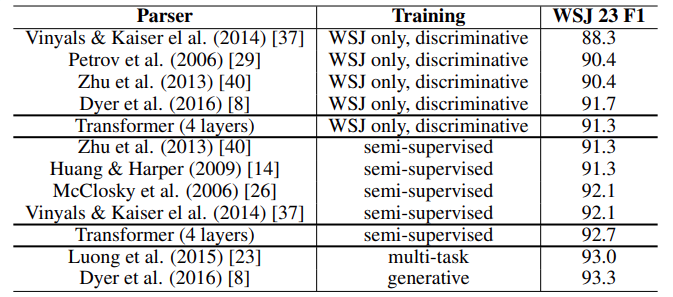
效果

Code精读
Input Embedding的官方pytorch实现
# mypy: allow-untyped-defs
from typing import Optional
import torch
from torch import Tensor
from torch.nn import functional as F, init
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
from .module import Module
__all__ = ["Embedding", "EmbeddingBag"]
class Embedding(Module):
r"""A simple lookup table that stores embeddings of a fixed dictionary and size.
This module is often used to store word embeddings and retrieve them using indices.
The input to the module is a list of indices, and the output is the corresponding
word embeddings.
Args:
num_embeddings (int): size of the dictionary of embeddings
embedding_dim (int): the size of each embedding vector
padding_idx (int, optional): If specified, the entries at :attr:`padding_idx` do not contribute to the gradient;
therefore, the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` is not updated during training,
i.e. it remains as a fixed "pad". For a newly constructed Embedding,
the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` will default to all zeros,
but can be updated to another value to be used as the padding vector.
max_norm (float, optional): If given, each embedding vector with norm larger than :attr:`max_norm`
is renormalized to have norm :attr:`max_norm`.
norm_type (float, optional): The p of the p-norm to compute for the :attr:`max_norm` option. Default ``2``.
scale_grad_by_freq (bool, optional): If given, this will scale gradients by the inverse of frequency of
the words in the mini-batch. Default ``False``.
sparse (bool, optional): If ``True``, gradient w.r.t. :attr:`weight` matrix will be a sparse tensor.
See Notes for more details regarding sparse gradients.
Attributes:
weight (Tensor): the learnable weights of the module of shape (num_embeddings, embedding_dim)
initialized from :math:`\mathcal{N}(0, 1)`
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(*)`, IntTensor or LongTensor of arbitrary shape containing the indices to extract
- Output: :math:`(*, H)`, where `*` is the input shape and :math:`H=\text{embedding\_dim}`
.. note::
Keep in mind that only a limited number of optimizers support
sparse gradients: currently it's :class:`optim.SGD` (`CUDA` and `CPU`),
:class:`optim.SparseAdam` (`CUDA` and `CPU`) and :class:`optim.Adagrad` (`CPU`)
.. note::
When :attr:`max_norm` is not ``None``, :class:`Embedding`'s forward method will modify the
:attr:`weight` tensor in-place. Since tensors needed for gradient computations cannot be
modified in-place, performing a differentiable operation on ``Embedding.weight`` before
calling :class:`Embedding`'s forward method requires cloning ``Embedding.weight`` when
:attr:`max_norm` is not ``None``. For example::
n, d, m = 3, 5, 7
embedding = nn.Embedding(n, d, max_norm=1.0)
W = torch.randn((m, d), requires_grad=True)
idx = torch.tensor([1, 2])
a = embedding.weight.clone() @ W.t() # weight must be cloned for this to be differentiable
b = embedding(idx) @ W.t() # modifies weight in-place
out = (a.unsqueeze(0) + b.unsqueeze(1))
loss = out.sigmoid().prod()
loss.backward()
Examples::
>>> # an Embedding module containing 10 tensors of size 3
>>> embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3)
>>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each
>>> input = torch.LongTensor([[1, 2, 4, 5], [4, 3, 2, 9]])
>>> # xdoctest: +IGNORE_WANT("non-deterministic")
>>> embedding(input)
tensor([[[-0.0251, -1.6902, 0.7172],
[-0.6431, 0.0748, 0.6969],
[ 1.4970, 1.3448, -0.9685],
[-0.3677, -2.7265, -0.1685]],
[[ 1.4970, 1.3448, -0.9685],
[ 0.4362, -0.4004, 0.9400],
[-0.6431, 0.0748, 0.6969],
[ 0.9124, -2.3616, 1.1151]]])
>>> # example with padding_idx
>>> embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3, padding_idx=0)
>>> input = torch.LongTensor([[0, 2, 0, 5]])
>>> embedding(input)
tensor([[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.1535, -2.0309, 0.9315],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.1655, 0.9897, 0.0635]]])
>>> # example of changing `pad` vector
>>> padding_idx = 0
>>> embedding = nn.Embedding(3, 3, padding_idx=padding_idx)
>>> embedding.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.7895, -0.7089, -0.0364],
[ 0.6778, 0.5803, 0.2678]], requires_grad=True)
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... embedding.weight[padding_idx] = torch.ones(3)
>>> embedding.weight
Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000],
[-0.7895, -0.7089, -0.0364],
[ 0.6778, 0.5803, 0.2678]], requires_grad=True)
"""
__constants__ = [
"num_embeddings",
"embedding_dim",
"padding_idx",
"max_norm",
"norm_type",
"scale_grad_by_freq",
"sparse",
]
num_embeddings: int
embedding_dim: int
padding_idx: Optional[int]
max_norm: Optional[float]
norm_type: float
scale_grad_by_freq: bool
weight: Tensor
freeze: bool
sparse: bool
def __init__(
self,
num_embeddings: int,
embedding_dim: int,
padding_idx: Optional[int] = None,
max_norm: Optional[float] = None,
norm_type: float = 2.0,
scale_grad_by_freq: bool = False,
sparse: bool = False,
_weight: Optional[Tensor] = None,
_freeze: bool = False,
device=None,
dtype=None,
) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.num_embeddings = num_embeddings
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
if padding_idx is not None:
if padding_idx > 0:
assert (
padding_idx < self.num_embeddings
), "Padding_idx must be within num_embeddings"
elif padding_idx < 0:
assert (
padding_idx >= -self.num_embeddings
), "Padding_idx must be within num_embeddings"
padding_idx = self.num_embeddings + padding_idx
self.padding_idx = padding_idx
self.max_norm = max_norm
self.norm_type = norm_type
self.scale_grad_by_freq = scale_grad_by_freq
if _weight is None:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((num_embeddings, embedding_dim), **factory_kwargs),
requires_grad=not _freeze,
)
self.reset_parameters()
else:
assert list(_weight.shape) == [
num_embeddings,
embedding_dim,
], "Shape of weight does not match num_embeddings and embedding_dim"
self.weight = Parameter(_weight, requires_grad=not _freeze)
self.sparse = sparse
def reset_parameters(self) -> None:
init.normal_(self.weight)
self._fill_padding_idx_with_zero()
def _fill_padding_idx_with_zero(self) -> None:
if self.padding_idx is not None:
with torch.no_grad():
self.weight[self.padding_idx].fill_(0)
def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return F.embedding(
input,
self.weight,
self.padding_idx,
self.max_norm,
self.norm_type,
self.scale_grad_by_freq,
self.sparse,
)
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
s = "{num_embeddings}, {embedding_dim}"
if self.padding_idx is not None:
s += ", padding_idx={padding_idx}"
if self.max_norm is not None:
s += ", max_norm={max_norm}"
if self.norm_type != 2:
s += ", norm_type={norm_type}"
if self.scale_grad_by_freq is not False:
s += ", scale_grad_by_freq={scale_grad_by_freq}"
if self.sparse is not False:
s += ", sparse=True"
return s.format(**self.__dict__)
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(
cls,
embeddings,
freeze=True,
padding_idx=None,
max_norm=None,
norm_type=2.0,
scale_grad_by_freq=False,
sparse=False,
):
r"""Create Embedding instance from given 2-dimensional FloatTensor.
Args:
embeddings (Tensor): FloatTensor containing weights for the Embedding.
First dimension is being passed to Embedding as ``num_embeddings``, second as ``embedding_dim``.
freeze (bool, optional): If ``True``, the tensor does not get updated in the learning process.
Equivalent to ``embedding.weight.requires_grad = False``. Default: ``True``
padding_idx (int, optional): If specified, the entries at :attr:`padding_idx` do not contribute to the gradient;
therefore, the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` is not updated during training,
i.e. it remains as a fixed "pad".
max_norm (float, optional): See module initialization documentation.
norm_type (float, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default ``2``.
scale_grad_by_freq (bool, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default ``False``.
sparse (bool, optional): See module initialization documentation.
Examples::
>>> # FloatTensor containing pretrained weights
>>> weight = torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2.3, 3], [4, 5.1, 6.3]])
>>> embedding = nn.Embedding.from_pretrained(weight)
>>> # Get embeddings for index 1
>>> input = torch.LongTensor([1])
>>> # xdoctest: +IGNORE_WANT("non-deterministic")
>>> embedding(input)
tensor([[ 4.0000, 5.1000, 6.3000]])
"""
assert (
embeddings.dim() == 2
), "Embeddings parameter is expected to be 2-dimensional"
rows, cols = embeddings.shape
embedding = cls(
num_embeddings=rows,
embedding_dim=cols,
_weight=embeddings,
_freeze=freeze,
padding_idx=padding_idx,
max_norm=max_norm,
norm_type=norm_type,
scale_grad_by_freq=scale_grad_by_freq,
sparse=sparse,
)
return embedding
class EmbeddingBag(Module):
r"""Compute sums or means of 'bags' of embeddings, without instantiating the intermediate embeddings.
For bags of constant length, no :attr:`per_sample_weights`, no indices equal to :attr:`padding_idx`,
and with 2D inputs, this class
* with ``mode="sum"`` is equivalent to :class:`~torch.nn.Embedding` followed by ``torch.sum(dim=1)``,
* with ``mode="mean"`` is equivalent to :class:`~torch.nn.Embedding` followed by ``torch.mean(dim=1)``,
* with ``mode="max"`` is equivalent to :class:`~torch.nn.Embedding` followed by ``torch.max(dim=1)``.
However, :class:`~torch.nn.EmbeddingBag` is much more time and memory efficient than using a chain of these
operations.
EmbeddingBag also supports per-sample weights as an argument to the forward
pass. This scales the output of the Embedding before performing a weighted
reduction as specified by ``mode``. If :attr:`per_sample_weights` is passed, the
only supported ``mode`` is ``"sum"``, which computes a weighted sum according to
:attr:`per_sample_weights`.
Args:
num_embeddings (int): size of the dictionary of embeddings
embedding_dim (int): the size of each embedding vector
max_norm (float, optional): If given, each embedding vector with norm larger than :attr:`max_norm`
is renormalized to have norm :attr:`max_norm`.
norm_type (float, optional): The p of the p-norm to compute for the :attr:`max_norm` option. Default ``2``.
scale_grad_by_freq (bool, optional): if given, this will scale gradients by the inverse of frequency of
the words in the mini-batch. Default ``False``.
Note: this option is not supported when ``mode="max"``.
mode (str, optional): ``"sum"``, ``"mean"`` or ``"max"``. Specifies the way to reduce the bag.
``"sum"`` computes the weighted sum, taking :attr:`per_sample_weights`
into consideration. ``"mean"`` computes the average of the values
in the bag, ``"max"`` computes the max value over each bag.
Default: ``"mean"``
sparse (bool, optional): if ``True``, gradient w.r.t. :attr:`weight` matrix will be a sparse tensor. See
Notes for more details regarding sparse gradients. Note: this option is not
supported when ``mode="max"``.
include_last_offset (bool, optional): if ``True``, :attr:`offsets` has one additional element, where the last element
is equivalent to the size of `indices`. This matches the CSR format.
padding_idx (int, optional): If specified, the entries at :attr:`padding_idx` do not contribute to the
gradient; therefore, the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` is not updated
during training, i.e. it remains as a fixed "pad". For a newly constructed
EmbeddingBag, the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` will default to all
zeros, but can be updated to another value to be used as the padding vector.
Note that the embedding vector at :attr:`padding_idx` is excluded from the
reduction.
Attributes:
weight (Tensor): the learnable weights of the module of shape `(num_embeddings, embedding_dim)`
initialized from :math:`\mathcal{N}(0, 1)`.
Examples::
>>> # an EmbeddingBag module containing 10 tensors of size 3
>>> embedding_sum = nn.EmbeddingBag(10, 3, mode='sum')
>>> # a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each
>>> input = torch.tensor([1, 2, 4, 5, 4, 3, 2, 9], dtype=torch.long)
>>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 4], dtype=torch.long)
>>> # xdoctest: +IGNORE_WANT("non-deterministic")
>>> embedding_sum(input, offsets)
tensor([[-0.8861, -5.4350, -0.0523],
[ 1.1306, -2.5798, -1.0044]])
>>> # Example with padding_idx
>>> embedding_sum = nn.EmbeddingBag(10, 3, mode='sum', padding_idx=2)
>>> input = torch.tensor([2, 2, 2, 2, 4, 3, 2, 9], dtype=torch.long)
>>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 4], dtype=torch.long)
>>> embedding_sum(input, offsets)
tensor([[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.7082, 3.2145, -2.6251]])
>>> # An EmbeddingBag can be loaded from an Embedding like so
>>> embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3, padding_idx=2)
>>> embedding_sum = nn.EmbeddingBag.from_pretrained(
embedding.weight,
padding_idx=embedding.padding_idx,
mode='sum')
"""
__constants__ = [
"num_embeddings",
"embedding_dim",
"max_norm",
"norm_type",
"scale_grad_by_freq",
"mode",
"sparse",
"include_last_offset",
"padding_idx",
]
num_embeddings: int
embedding_dim: int
max_norm: Optional[float]
norm_type: float
scale_grad_by_freq: bool
weight: Tensor
mode: str
sparse: bool
include_last_offset: bool
padding_idx: Optional[int]
def __init__(
self,
num_embeddings: int,
embedding_dim: int,
max_norm: Optional[float] = None,
norm_type: float = 2.0,
scale_grad_by_freq: bool = False,
mode: str = "mean",
sparse: bool = False,
_weight: Optional[Tensor] = None,
include_last_offset: bool = False,
padding_idx: Optional[int] = None,
device=None,
dtype=None,
) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.num_embeddings = num_embeddings
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.max_norm = max_norm
self.norm_type = norm_type
self.scale_grad_by_freq = scale_grad_by_freq
if padding_idx is not None:
if padding_idx > 0:
assert (
padding_idx < self.num_embeddings
), "padding_idx must be within num_embeddings"
elif padding_idx < 0:
assert (
padding_idx >= -self.num_embeddings
), "padding_idx must be within num_embeddings"
padding_idx = self.num_embeddings + padding_idx
self.padding_idx = padding_idx
if _weight is None:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((num_embeddings, embedding_dim), **factory_kwargs)
)
self.reset_parameters()
else:
assert list(_weight.shape) == [
num_embeddings,
embedding_dim,
], "Shape of weight does not match num_embeddings and embedding_dim"
self.weight = Parameter(_weight)
self.mode = mode
self.sparse = sparse
self.include_last_offset = include_last_offset
def reset_parameters(self) -> None:
init.normal_(self.weight)
self._fill_padding_idx_with_zero()
def _fill_padding_idx_with_zero(self) -> None:
if self.padding_idx is not None:
with torch.no_grad():
self.weight[self.padding_idx].fill_(0)
def forward(
self,
input: Tensor,
offsets: Optional[Tensor] = None,
per_sample_weights: Optional[Tensor] = None,
) -> Tensor:
"""Forward pass of EmbeddingBag.
Args:
input (Tensor): Tensor containing bags of indices into the embedding matrix.
offsets (Tensor, optional): Only used when :attr:`input` is 1D. :attr:`offsets` determines
the starting index position of each bag (sequence) in :attr:`input`.
per_sample_weights (Tensor, optional): a tensor of float / double weights, or None
to indicate all weights should be taken to be ``1``. If specified, :attr:`per_sample_weights`
must have exactly the same shape as input and is treated as having the same
:attr:`offsets`, if those are not ``None``. Only supported for ``mode='sum'``.
Returns:
Tensor output shape of `(B, embedding_dim)`.
.. note::
A few notes about ``input`` and ``offsets``:
- :attr:`input` and :attr:`offsets` have to be of the same type, either int or long
- If :attr:`input` is 2D of shape `(B, N)`, it will be treated as ``B`` bags (sequences)
each of fixed length ``N``, and this will return ``B`` values aggregated in a way
depending on the :attr:`mode`. :attr:`offsets` is ignored and required to be ``None`` in this case.
- If :attr:`input` is 1D of shape `(N)`, it will be treated as a concatenation of
multiple bags (sequences). :attr:`offsets` is required to be a 1D tensor containing the
starting index positions of each bag in :attr:`input`. Therefore, for :attr:`offsets` of shape `(B)`,
:attr:`input` will be viewed as having ``B`` bags. Empty bags (i.e., having 0-length) will have
returned vectors filled by zeros.
"""
return F.embedding_bag(
input,
self.weight,
offsets,
self.max_norm,
self.norm_type,
self.scale_grad_by_freq,
self.mode,
self.sparse,
per_sample_weights,
self.include_last_offset,
self.padding_idx,
)
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
s = "{num_embeddings}, {embedding_dim}"
if self.max_norm is not None:
s += ", max_norm={max_norm}"
if self.norm_type != 2:
s += ", norm_type={norm_type}"
if self.scale_grad_by_freq is not False:
s += ", scale_grad_by_freq={scale_grad_by_freq}"
s += ", mode={mode}"
if self.padding_idx is not None:
s += ", padding_idx={padding_idx}"
return s.format(**{k: repr(v) for k, v in self.__dict__.items()})
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(
cls,
embeddings: Tensor,
freeze: bool = True,
max_norm: Optional[float] = None,
norm_type: float = 2.0,
scale_grad_by_freq: bool = False,
mode: str = "mean",
sparse: bool = False,
include_last_offset: bool = False,
padding_idx: Optional[int] = None,
) -> "EmbeddingBag":
r"""Create EmbeddingBag instance from given 2-dimensional FloatTensor.
Args:
embeddings (Tensor): FloatTensor containing weights for the EmbeddingBag.
First dimension is being passed to EmbeddingBag as 'num_embeddings', second as 'embedding_dim'.
freeze (bool, optional): If ``True``, the tensor does not get updated in the learning process.
Equivalent to ``embeddingbag.weight.requires_grad = False``. Default: ``True``
max_norm (float, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default: ``None``
norm_type (float, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default ``2``.
scale_grad_by_freq (bool, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default ``False``.
mode (str, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default: ``"mean"``
sparse (bool, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default: ``False``.
include_last_offset (bool, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default: ``False``.
padding_idx (int, optional): See module initialization documentation. Default: ``None``.
Examples::
>>> # FloatTensor containing pretrained weights
>>> weight = torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2.3, 3], [4, 5.1, 6.3]])
>>> embeddingbag = nn.EmbeddingBag.from_pretrained(weight)
>>> # Get embeddings for index 1
>>> input = torch.LongTensor([[1, 0]])
>>> # xdoctest: +IGNORE_WANT("non-deterministic")
>>> embeddingbag(input)
tensor([[ 2.5000, 3.7000, 4.6500]])
"""
assert (
embeddings.dim() == 2
), "Embeddings parameter is expected to be 2-dimensional"
rows, cols = embeddings.shape
embeddingbag = cls(
num_embeddings=rows,
embedding_dim=cols,
_weight=embeddings,
max_norm=max_norm,
norm_type=norm_type,
scale_grad_by_freq=scale_grad_by_freq,
mode=mode,
sparse=sparse,
include_last_offset=include_last_offset,
padding_idx=padding_idx,
)
embeddingbag.weight.requires_grad = not freeze
return embeddingbag
缩放点积注意力(scaled_dot_product)的官方pytorch实现
# Efficient implementation equivalent to the following:
def scaled_dot_product_attention(query, key, value, attn_mask=None, dropout_p=0.0,
is_causal=False, scale=None, enable_gqa=False) -> torch.Tensor:
L, S = query.size(-2), key.size(-2)
scale_factor = 1 / math.sqrt(query.size(-1)) if scale is None else scale #1/sqrt{d_k}
attn_bias = torch.zeros(L, S, dtype=query.dtype)
if is_causal:#仅允许在当前时间步之前的时间步进行注意力计算,防止未来信息泄露
assert attn_mask is None
temp_mask = torch.ones(L, S, dtype=torch.bool).tril(diagonal=0)
attn_bias.masked_fill_(temp_mask.logical_not(), float("-inf"))
attn_bias.to(query.dtype)
if attn_mask is not None:
if attn_mask.dtype == torch.bool:
attn_bias.masked_fill_(attn_mask.logical_not(), float("-inf"))
else:
attn_bias += attn_mask
if enable_gqa:
key = key.repeat_interleave(query.size(-3)//key.size(-3), -3)#沿张量key的第-3维元素重复大小为query.size(-3)//key.size(-3)遍
value = value.repeat_interleave(query.size(-3)//value.size(-3), -3)
#math::Attention(Q, K, V) = softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k} })V
attn_weight = query @ key.transpose(-2, -1) * scale_factor# 最后一维和倒数第二维转置
attn_weight += attn_bias
attn_weight = torch.softmax(attn_weight, dim=-1)#计算最后一个维度的softmax
attn_weight = torch.dropout(attn_weight, dropout_p, train=True)#当 train=False 时,dropout 被禁用,所有元素都会被保留。
return attn_weight @ value
MultiheadAttention类pytorch官方实现
class MultiheadAttention(Module):
r"""Allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces.
Method described in the paper:
`Attention Is All You Need <https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762>`_.
Multi-Head Attention is defined as:
.. math::
\text{MultiHead}(Q, K, V) = \text{Concat}(head_1,\dots,head_h)W^O
where :math:`head_i = \text{Attention}(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V)`.
``nn.MultiHeadAttention`` will use the optimized implementations of
``scaled_dot_product_attention()`` when possible.
In addition to support for the new ``scaled_dot_product_attention()``
function, for speeding up Inference, MHA will use
fastpath inference with support for Nested Tensors, iff:
- self attention is being computed (i.e., ``query``, ``key``, and ``value`` are the same tensor).
- inputs are batched (3D) with ``batch_first==True``
- Either autograd is disabled (using ``torch.inference_mode`` or ``torch.no_grad``) or no tensor argument ``requires_grad``
- training is disabled (using ``.eval()``)
- ``add_bias_kv`` is ``False``
- ``add_zero_attn`` is ``False``
- ``kdim`` and ``vdim`` are equal to ``embed_dim``
- if a `NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_ is passed, neither ``key_padding_mask``
nor ``attn_mask`` is passed
- autocast is disabled
If the optimized inference fastpath implementation is in use, a
`NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_ can be passed for
``query``/``key``/``value`` to represent padding more efficiently than using a
padding mask. In this case, a `NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_
will be returned, and an additional speedup proportional to the fraction of the input
that is padding can be expected.
Args:
embed_dim: Total dimension of the model, d_{model}.
num_heads: Number of parallel attention heads. Note that ``embed_dim`` will be split
across ``num_heads`` (i.e. each head will have dimension ``embed_dim // num_heads``).
dropout: Dropout probability on ``attn_output_weights``. Default: ``0.0`` (no dropout).
bias: If specified, adds bias to input / output projection layers. Default: ``True``.
add_bias_kv: If specified, adds bias to the key and value sequences at dim=0. Default: ``False``.
add_zero_attn: If specified, adds a new batch of zeros to the key and value sequences at dim=1.
Default: ``False``.
kdim: Total number of features for keys. Default: ``None`` (uses ``kdim=embed_dim``).
vdim: Total number of features for values. Default: ``None`` (uses ``vdim=embed_dim``).
batch_first: If ``True``, then the input and output tensors are provided
as (batch, seq, feature). Default: ``False`` (seq, batch, feature).
Examples::
>>> # xdoctest: +SKIP
>>> multihead_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim, num_heads)
>>> attn_output, attn_output_weights = multihead_attn(query, key, value)
.. _`FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness`:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135
"""
__constants__ = ["batch_first"]
bias_k: Optional[torch.Tensor]
bias_v: Optional[torch.Tensor]
def __init__(
self,
embed_dim,
num_heads,
dropout=0.0,
bias=True,
add_bias_kv=False,
add_zero_attn=False,
kdim=None,
vdim=None,
batch_first=False,
device=None,
dtype=None,
) -> None:
if embed_dim <= 0 or num_heads <= 0:
raise ValueError(
f"embed_dim and num_heads must be greater than 0,"
f" got embed_dim={embed_dim} and num_heads={num_heads} instead"
)
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.kdim = kdim if kdim is not None else embed_dim
self.vdim = vdim if vdim is not None else embed_dim
self._qkv_same_embed_dim = self.kdim == embed_dim and self.vdim == embed_dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.dropout = dropout
self.batch_first = batch_first
self.head_dim = embed_dim // num_heads#每个头的维度
assert (
self.head_dim * num_heads == self.embed_dim
), "embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads"
if not self._qkv_same_embed_dim:
self.q_proj_weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((embed_dim, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs)
)
self.k_proj_weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((embed_dim, self.kdim), **factory_kwargs)
)
self.v_proj_weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((embed_dim, self.vdim), **factory_kwargs)
)
self.register_parameter("in_proj_weight", None)
else:
self.in_proj_weight = Parameter(
torch.empty((3 * embed_dim, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs)
)
self.register_parameter("q_proj_weight", None)
self.register_parameter("k_proj_weight", None)
self.register_parameter("v_proj_weight", None)
if bias:
self.in_proj_bias = Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim, **factory_kwargs))
else:
self.register_parameter("in_proj_bias", None)
self.out_proj = NonDynamicallyQuantizableLinear(
embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs
)
if add_bias_kv:
self.bias_k = Parameter(torch.empty((1, 1, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))
self.bias_v = Parameter(torch.empty((1, 1, embed_dim), **factory_kwargs))
else:
self.bias_k = self.bias_v = None
self.add_zero_attn = add_zero_attn
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
if self._qkv_same_embed_dim:
xavier_uniform_(self.in_proj_weight)#xavier_uniform_通过均匀分布初始化权重,使得每一层的输入和输出的方差大致相同,有助于避免梯度消失或爆炸
else:
xavier_uniform_(self.q_proj_weight)
xavier_uniform_(self.k_proj_weight)
xavier_uniform_(self.v_proj_weight)
if self.in_proj_bias is not None:
#将这些偏置项初始化为常数 0.0,通常偏置项初始化为零能有效地帮助训练的收敛性
constant_(self.in_proj_bias, 0.0)
constant_(self.out_proj.bias, 0.0)
if self.bias_k is not None:
xavier_normal_(self.bias_k)
if self.bias_v is not None:
xavier_normal_(self.bias_v)
def __setstate__(self, state):
# Support loading old MultiheadAttention checkpoints generated by v1.1.0
if "_qkv_same_embed_dim" not in state:
state["_qkv_same_embed_dim"] = True
super().__setstate__(state)
def forward(
self,
query: Tensor,
key: Tensor,
value: Tensor,
key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
need_weights: bool = True,
attn_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
average_attn_weights: bool = True,
is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Optional[Tensor]]:
r"""Compute attention outputs using query, key, and value embeddings.
Supports optional parameters for padding, masks and attention weights.
Args:
query: Query embeddings of shape :math:`(L, E_q)` for unbatched input, :math:`(L, N, E_q)` when ``batch_first=False``
or :math:`(N, L, E_q)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`L` is the target sequence length,
:math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_q` is the query embedding dimension ``embed_dim``.
Queries are compared against key-value pairs to produce the output.
See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.
key: Key embeddings of shape :math:`(S, E_k)` for unbatched input, :math:`(S, N, E_k)` when ``batch_first=False``
or :math:`(N, S, E_k)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`S` is the source sequence length,
:math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_k` is the key embedding dimension ``kdim``.
See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.
value: Value embeddings of shape :math:`(S, E_v)` for unbatched input, :math:`(S, N, E_v)` when
``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, S, E_v)` when ``batch_first=True``, where :math:`S` is the source
sequence length, :math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E_v` is the value embedding dimension ``vdim``.
See "Attention Is All You Need" for more details.
key_padding_mask: If specified, a mask of shape :math:`(N, S)` indicating which elements within ``key``
to ignore for the purpose of attention (i.e. treat as "padding"). For unbatched `query`, shape should be :math:`(S)`.
Binary and float masks are supported.
For a binary mask, a ``True`` value indicates that the corresponding ``key`` value will be ignored for
the purpose of attention. For a float mask, it will be directly added to the corresponding ``key`` value.
need_weights: If specified, returns ``attn_output_weights`` in addition to ``attn_outputs``.
Set ``need_weights=False`` to use the optimized ``scaled_dot_product_attention``
and achieve the best performance for MHA.
Default: ``True``.
attn_mask: If specified, a 2D or 3D mask preventing attention to certain positions. Must be of shape
:math:`(L, S)` or :math:`(N\cdot\text{num\_heads}, L, S)`, where :math:`N` is the batch size,
:math:`L` is the target sequence length, and :math:`S` is the source sequence length. A 2D mask will be
broadcasted across the batch while a 3D mask allows for a different mask for each entry in the batch.
Binary and float masks are supported. For a binary mask, a ``True`` value indicates that the
corresponding position is not allowed to attend. For a float mask, the mask values will be added to
the attention weight.
If both attn_mask and key_padding_mask are supplied, their types should match.
average_attn_weights: If true, indicates that the returned ``attn_weights`` should be averaged across
heads. Otherwise, ``attn_weights`` are provided separately per head. Note that this flag only has an
effect when ``need_weights=True``. Default: ``True`` (i.e. average weights across heads)
is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as attention mask.
Default: ``False``.
Warning:
``is_causal`` provides a hint that ``attn_mask`` is the
causal mask. Providing incorrect hints can result in
incorrect execution, including forward and backward
compatibility.
Outputs:
- **attn_output** - Attention outputs of shape :math:`(L, E)` when input is unbatched,
:math:`(L, N, E)` when ``batch_first=False`` or :math:`(N, L, E)` when ``batch_first=True``,
where :math:`L` is the target sequence length, :math:`N` is the batch size, and :math:`E` is the
embedding dimension ``embed_dim``.
- **attn_output_weights** - Only returned when ``need_weights=True``. If ``average_attn_weights=True``,
returns attention weights averaged across heads of shape :math:`(L, S)` when input is unbatched or
:math:`(N, L, S)`, where :math:`N` is the batch size, :math:`L` is the target sequence length, and
:math:`S` is the source sequence length. If ``average_attn_weights=False``, returns attention weights per
head of shape :math:`(\text{num\_heads}, L, S)` when input is unbatched or :math:`(N, \text{num\_heads}, L, S)`.
.. note::
`batch_first` argument is ignored for unbatched inputs.
""" # noqa: B950
why_not_fast_path = ""
if (
(attn_mask is not None and torch.is_floating_point(attn_mask))
or (key_padding_mask is not None)
and torch.is_floating_point(key_padding_mask)
):
why_not_fast_path = "floating-point masks are not supported for fast path."
is_batched = query.dim() == 3
key_padding_mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=key_padding_mask,
mask_name="key_padding_mask",
other_type=F._none_or_dtype(attn_mask),
other_name="attn_mask",
target_type=query.dtype,
)
attn_mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=attn_mask,
mask_name="attn_mask",
other_type=None,
other_name="",
target_type=query.dtype,
check_other=False,
)
is_fastpath_enabled = torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled()
if not is_fastpath_enabled:
why_not_fast_path = "torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled() was not True"
elif not is_batched:
why_not_fast_path = (
f"input not batched; expected query.dim() of 3 but got {query.dim()}"
)
elif query is not key or key is not value:
# When lifting this restriction, don't forget to either
# enforce that the dtypes all match or test cases where
# they don't!
why_not_fast_path = "non-self attention was used (query, key, and value are not the same Tensor)"
elif self.in_proj_bias is not None and query.dtype != self.in_proj_bias.dtype:
why_not_fast_path = f"dtypes of query ({query.dtype}) and self.in_proj_bias ({self.in_proj_bias.dtype}) don't match"
elif self.in_proj_weight is None:
why_not_fast_path = "in_proj_weight was None"
elif query.dtype != self.in_proj_weight.dtype:
# this case will fail anyway, but at least they'll get a useful error message.
why_not_fast_path = f"dtypes of query ({query.dtype}) and self.in_proj_weight ({self.in_proj_weight.dtype}) don't match"
elif self.training:
why_not_fast_path = "training is enabled"
elif (self.num_heads % 2) != 0:
why_not_fast_path = "self.num_heads is not even"
elif not self.batch_first:
why_not_fast_path = "batch_first was not True"
elif self.bias_k is not None:
why_not_fast_path = "self.bias_k was not None"
elif self.bias_v is not None:
why_not_fast_path = "self.bias_v was not None"
elif self.add_zero_attn:
why_not_fast_path = "add_zero_attn was enabled"
elif not self._qkv_same_embed_dim:
why_not_fast_path = "_qkv_same_embed_dim was not True"
elif query.is_nested and (
key_padding_mask is not None or attn_mask is not None
):
why_not_fast_path = "supplying both src_key_padding_mask and src_mask at the same time \
is not supported with NestedTensor input"
elif torch.is_autocast_enabled():
why_not_fast_path = "autocast is enabled"
if not why_not_fast_path:
tensor_args = (
query,
key,
value,
self.in_proj_weight,
self.in_proj_bias,
self.out_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.bias,
)
# We have to use list comprehensions below because TorchScript does not support
# generator expressions.
if torch.overrides.has_torch_function(tensor_args):
why_not_fast_path = "some Tensor argument has_torch_function"
elif _is_make_fx_tracing():
why_not_fast_path = "we are running make_fx tracing"
elif not all(_check_arg_device(x) for x in tensor_args):
why_not_fast_path = (
"some Tensor argument's device is neither one of "
f"cpu, cuda or {torch.utils.backend_registration._privateuse1_backend_name}"
)
elif torch.is_grad_enabled() and any(
_arg_requires_grad(x) for x in tensor_args
):
why_not_fast_path = (
"grad is enabled and at least one of query or the "
"input/output projection weights or biases requires_grad"
)
if not why_not_fast_path:
merged_mask, mask_type = self.merge_masks(
attn_mask, key_padding_mask, query
)
if self.in_proj_bias is not None and self.in_proj_weight is not None:
return torch._native_multi_head_attention(
query,
key,
value,
self.embed_dim,
self.num_heads,
self.in_proj_weight,
self.in_proj_bias,
self.out_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.bias,
merged_mask,
need_weights,
average_attn_weights,
mask_type,
)
any_nested = query.is_nested or key.is_nested or value.is_nested
assert not any_nested, (
"MultiheadAttention does not support NestedTensor outside of its fast path. "
+ f"The fast path was not hit because {why_not_fast_path}"
)
if self.batch_first and is_batched:
# make sure that the transpose op does not affect the "is" property
if key is value:
if query is key:
query = key = value = query.transpose(1, 0)
else:
query, key = (x.transpose(1, 0) for x in (query, key))
value = key
else:
query, key, value = (x.transpose(1, 0) for x in (query, key, value))
if not self._qkv_same_embed_dim:
attn_output, attn_output_weights = F.multi_head_attention_forward(
query,
key,
value,
self.embed_dim,
self.num_heads,
self.in_proj_weight,
self.in_proj_bias,
self.bias_k,
self.bias_v,
self.add_zero_attn,
self.dropout,
self.out_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.bias,
training=self.training,
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
need_weights=need_weights,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
use_separate_proj_weight=True,
q_proj_weight=self.q_proj_weight,
k_proj_weight=self.k_proj_weight,
v_proj_weight=self.v_proj_weight,
average_attn_weights=average_attn_weights,
is_causal=is_causal,
)
else:
attn_output, attn_output_weights = F.multi_head_attention_forward(
query,
key,
value,
self.embed_dim,
self.num_heads,
self.in_proj_weight,
self.in_proj_bias,
self.bias_k,
self.bias_v,
self.add_zero_attn,
self.dropout,
self.out_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.bias,
training=self.training,
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
need_weights=need_weights,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
average_attn_weights=average_attn_weights,
is_causal=is_causal,
)
if self.batch_first and is_batched:
return attn_output.transpose(1, 0), attn_output_weights
else:
return attn_output, attn_output_weights
def merge_masks(
self,
attn_mask: Optional[Tensor],
key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor],
query: Tensor,
) -> Tuple[Optional[Tensor], Optional[int]]:
r"""Determine mask type and combine masks if necessary.
If only one mask is provided, that mask
and the corresponding mask type will be returned. If both masks are provided, they will be both
expanded to shape ``(batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, seq_len)``, combined with logical ``or``
and mask type 2 will be returned
Args:
attn_mask: attention mask of shape ``(seq_len, seq_len)``, mask type 0
key_padding_mask: padding mask of shape ``(batch_size, seq_len)``, mask type 1
query: query embeddings of shape ``(batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim)``
Returns:
merged_mask: merged mask
mask_type: merged mask type (0, 1, or 2)
"""
mask_type: Optional[int] = None
merged_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None
if key_padding_mask is not None:
mask_type = 1
merged_mask = key_padding_mask
if attn_mask is not None:
# In this branch query can't be a nested tensor, so it has a shape
batch_size, seq_len, _ = query.shape
mask_type = 2
# Always expands attn_mask to 4D
if attn_mask.dim() == 3:
attn_mask_expanded = attn_mask.view(batch_size, -1, seq_len, seq_len)
else: # attn_mask.dim() == 2:
attn_mask_expanded = attn_mask.view(1, 1, seq_len, seq_len).expand(
batch_size, self.num_heads, -1, -1
)
merged_mask = attn_mask_expanded
if key_padding_mask is not None:
key_padding_mask_expanded = key_padding_mask.view(
batch_size, 1, 1, seq_len
).expand(-1, self.num_heads, -1, -1)
merged_mask = attn_mask_expanded + key_padding_mask_expanded
# no attn_mask and no key_padding_mask, returns None, None
return merged_mask, mask_type
逐点前馈网络(Position-wise Feed-forward Networks)的官方pytorch实现
d_{model}=512
dim_feedforward: int = 2048
self.linear1 = Linear(d_{model}, dim_feedforward, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.dropout = Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = Linear(dim_feedforward, d_{model}, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
编码器的官方pytorch实现
嵌套张量(Nested Tensor):
-
嵌套张量(Nested Tensor) 是一种特殊的数据结构,它可以处理具有不同长度的序列(例如不同长度的句子或不同大小的图像)。这种结构对于处理不规则的序列数据非常有用,特别是在处理包含填充(padding)的批次数据时。
-
默认情况下,
TransformerEncoder会使用常规的张量(Tensor)作为输入,这要求所有的序列(例如一个批次中的多个句子)具有相同的长度。若序列的长度不一致,需要填充(padding)以使它们对齐。这在很多情况下可能导致不必要的计算浪费。 -
enable_nested_tensor=True时,输入数据将自动转换为嵌套张量。嵌套张量能够灵活地处理不同长度的序列,它会在内部以更加高效的方式存储不规则序列的数据,减少对填充的依赖,从而提升性能。尤其是在填充率较高时,使用嵌套张量能显著减少计算量并提高性能。
稀疏路径加速(sparsity fast path)
- 目的:主要用于加速稀疏数据的计算
- 触发条件:只要有一个条件不满足,就不会启用 “sparsity fast path”
- 编码层的实例化:encoder_layer 必须是 TransformerEncoderLayer。
- 归一化层的配置:(norm_first)在注意力机制之前不使用归一化。
- 批处理顺序:batch_first批处理维度在最前面。
- 嵌入维度一致性(
_qkv_same_embed_dim是否为True):自注意力中的查询、键、值的嵌入维度应该相同。 - 自注意力机制中的偏置和激活函数的设置:有in_proj_bias偏置项,激活函数是 ReLU 或 GELU
- 注意力头数奇偶性:必须是偶数。
class TransformerEncoder(Module):
r"""TransformerEncoder is a stack of N encoder layers.
.. note::
See `this tutorial <https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/transformer_building_blocks.html>`_
for an in depth discussion of the performant building blocks PyTorch offers for building your own
transformer layers.
Users can build the BERT(https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) model with corresponding parameters.
Args:
encoder_layer: an instance of the TransformerEncoderLayer() class (required).
num_layers: the number of sub-encoder-layers in the encoder (required).
norm: the layer normalization component (optional).
enable_nested_tensor: if True, input will automatically convert to nested tensor
(and convert back on output). This will improve the overall performance of
TransformerEncoder when padding rate is high. Default: ``True`` (enabled).
Examples::
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_{model}=512, nhead=8)
>>> transformer_encoder = nn.TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers=6)
>>> src = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> out = transformer_encoder(src)
"""
__constants__ = ["norm"]
def __init__(
self,
encoder_layer: "TransformerEncoderLayer",
num_layers: int,
norm: Optional[Module] = None,
enable_nested_tensor: bool = True,
mask_check: bool = True,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
torch._C._log_api_usage_once(f"torch.nn.modules.{self.__class__.__name__}")#torch._C._log_api_usage_once 是一个内部统计功能,用于记录和追踪 "torch.nn.modules.TransformerEncoder" 的使用频率
self.layers = _get_clones(encoder_layer, num_layers)#复制N层编码层
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.norm = norm#默认层归一化
# this attribute saves the value providedat object construction
self.enable_nested_tensor = enable_nested_tensor
# this attribute controls whether nested tensors are used 如果 self.use_nested_tensor 为 True,则模型会使用嵌套张量的优化路径,否则使用传统的张量结构进行计算
self.use_nested_tensor = enable_nested_tensor
self.mask_check = mask_check
enc_layer = "encoder_layer"
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = ""
if not isinstance(encoder_layer, torch.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = f"{enc_layer} was not TransformerEncoderLayer"
elif encoder_layer.norm_first:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = f"{enc_layer}.norm_first was True"
elif not encoder_layer.self_attn.batch_first:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"{enc_layer}.self_attn.batch_first was not True"
+ "(use batch_first for better inference performance)"
)
elif not encoder_layer.self_attn._qkv_same_embed_dim:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"{enc_layer}.self_attn._qkv_same_embed_dim was not True"
)
elif encoder_layer.self_attn.in_proj_bias is None:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = f"{enc_layer}.self_attn was passed bias=False"
elif not encoder_layer.activation_relu_or_gelu:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"{enc_layer}.activation_relu_or_gelu was not True"
)
elif not (encoder_layer.norm1.eps == encoder_layer.norm2.eps):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"{enc_layer}.norm1.eps was not equal to {enc_layer}.norm2.eps"
)
elif encoder_layer.self_attn.num_heads % 2 == 1:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = f"{enc_layer}.self_attn.num_heads is odd"
if enable_nested_tensor and why_not_sparsity_fast_path:
warnings.warn(
f"enable_nested_tensor is True, but self.use_nested_tensor is False because {why_not_sparsity_fast_path}"
)
self.use_nested_tensor = False
def forward(
self,
src: Tensor,
mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
src_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
is_causal: Optional[bool] = None,
) -> Tensor:
r"""Pass the input through the encoder layers in turn.
Args:
src: the sequence to the encoder (required).
mask: the mask for the src sequence (optional).
src_key_padding_mask: the mask for the src keys per batch (optional).
is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as ``mask``.
Default: ``None``; try to detect a causal mask.
Warning:
``is_causal`` provides a hint that ``mask`` is the
causal mask. Providing incorrect hints can result in
incorrect execution, including forward and backward
compatibility.
Shape:
see the docs in :class:`~torch.nn.Transformer`.
"""
#屏蔽填充位置
src_key_padding_mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=src_key_padding_mask,
mask_name="src_key_padding_mask",
other_type=F._none_or_dtype(mask),
other_name="mask",
target_type=src.dtype,
)
mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=mask,
mask_name="mask",
other_type=None,
other_name="",
target_type=src.dtype,
check_other=False,
)
output = src
convert_to_nested = False
first_layer = self.layers[0]
src_key_padding_mask_for_layers = src_key_padding_mask
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = ""
str_first_layer = "self.layers[0]"
batch_first = first_layer.self_attn.batch_first
is_fastpath_enabled = torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled()#mha (Multi-Head Attention)
if not is_fastpath_enabled:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled() was not True"
)
elif not hasattr(self, "use_nested_tensor"):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "use_nested_tensor attribute not present"
elif not self.use_nested_tensor:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"self.use_nested_tensor (set in init) was not True"
)
elif first_layer.training:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = f"{str_first_layer} was in training mode"
elif not src.dim() == 3:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"input not batched; expected src.dim() of 3 but got {src.dim()}"
)
elif src_key_padding_mask is None:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "src_key_padding_mask was None"
elif (
(not hasattr(self, "mask_check")) or self.mask_check
) and not torch._nested_tensor_from_mask_left_aligned(
src, src_key_padding_mask.logical_not()
):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "mask_check enabled, and src and src_key_padding_mask was not left aligned"
elif output.is_nested:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "NestedTensor input is not supported"
elif mask is not None:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"src_key_padding_mask and mask were both supplied"
)
elif torch.is_autocast_enabled():
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "autocast is enabled"
if not why_not_sparsity_fast_path:
tensor_args = (
src,
first_layer.self_attn.in_proj_weight,
first_layer.self_attn.in_proj_bias,
first_layer.self_attn.out_proj.weight,
first_layer.self_attn.out_proj.bias,
first_layer.norm1.weight,
first_layer.norm1.bias,
first_layer.norm2.weight,
first_layer.norm2.bias,
first_layer.linear1.weight,
first_layer.linear1.bias,
first_layer.linear2.weight,
first_layer.linear2.bias,
)
_supported_device_type = [
"cpu",
"cuda",
torch.utils.backend_registration._privateuse1_backend_name,
]
if torch.overrides.has_torch_function(tensor_args):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "some Tensor argument has_torch_function"
elif src.device.type not in _supported_device_type:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"src device is neither one of {_supported_device_type}"
)
elif torch.is_grad_enabled() and any(x.requires_grad for x in tensor_args):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"grad is enabled and at least one of query or the "
"input/output projection weights or biases requires_grad"
)
if (not why_not_sparsity_fast_path) and (src_key_padding_mask is not None):
convert_to_nested = True
output = torch._nested_tensor_from_mask(
output, src_key_padding_mask.logical_not(), mask_check=False
)
src_key_padding_mask_for_layers = None
seq_len = _get_seq_len(src, batch_first)
is_causal = _detect_is_causal_mask(mask, is_causal, seq_len)
for mod in self.layers:
output = mod(
output,
src_mask=mask,
is_causal=is_causal,
src_key_padding_mask=src_key_padding_mask_for_layers,
)
if convert_to_nested:
output = output.to_padded_tensor(0.0, src.size())
if self.norm is not None:
output = self.norm(output)
return output
编码器中的每一层TransformerEncoderLayer的pytorch官方实现
class TransformerEncoderLayer(Module):
r"""TransformerEncoderLayer is made up of self-attn and feedforward network.
.. note::
See `this tutorial <https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/transformer_building_blocks.html>`_
for an in depth discussion of the performant building blocks PyTorch offers for building your own
transformer layers.
This standard encoder layer is based on the paper "Attention Is All You Need".
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez,
Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 6000-6010. Users may modify or implement
in a different way during application.
TransformerEncoderLayer can handle either traditional torch.tensor inputs,
or Nested Tensor inputs. Derived classes are expected to similarly accept
both input formats. (Not all combinations of inputs are currently
supported by TransformerEncoderLayer while Nested Tensor is in prototype
state.)
If you are implementing a custom layer, you may derive it either from
the Module or TransformerEncoderLayer class. If your custom layer
supports both torch.Tensors and Nested Tensors inputs, make its
implementation a derived class of TransformerEncoderLayer. If your custom
Layer supports only torch.Tensor inputs, derive its implementation from
Module.
Args:
d_model: the number of expected features in the input (required).
nhead: the number of heads in the multiheadattention models (required).
dim_feedforward: the dimension of the feedforward network model (default=2048).
dropout: the dropout value (default=0.1).
activation: the activation function of the intermediate layer, can be a string
("relu" or "gelu") or a unary callable. Default: relu
layer_norm_eps: the eps value in layer normalization components (default=1e-5).
batch_first: If ``True``, then the input and output tensors are provided
as (batch, seq, feature). Default: ``False`` (seq, batch, feature).
norm_first: if ``True``, layer norm is done prior to attention and feedforward如果为 True,则在自注意力和前馈层前应用层归一化,否则在层之后应用
operations, respectively. Otherwise it's done after. Default: ``False`` (after).
bias: If set to ``False``, ``Linear`` and ``LayerNorm`` layers will not learn an additive
bias. Default: ``True``.
Examples::
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8)
>>> src = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> out = encoder_layer(src)
Alternatively, when ``batch_first`` is ``True``:
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8, batch_first=True)
>>> src = torch.rand(32, 10, 512)
>>> out = encoder_layer(src)
Fast path:
forward() will use a special optimized implementation described in
`FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness`_ if all of the following
conditions are met:
- Either autograd is disabled (using ``torch.inference_mode`` or ``torch.no_grad``) or no tensor
argument ``requires_grad``
- training is disabled (using ``.eval()``)
- batch_first is ``True`` and the input is batched (i.e., ``src.dim() == 3``)
- activation is one of: ``"relu"``, ``"gelu"``, ``torch.functional.relu``, or ``torch.functional.gelu``
- at most one of ``src_mask`` and ``src_key_padding_mask`` is passed
- if src is a `NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_, neither ``src_mask``
nor ``src_key_padding_mask`` is passed
- the two ``LayerNorm`` instances have a consistent ``eps`` value (this will naturally be the case
unless the caller has manually modified one without modifying the other)
If the optimized implementation is in use, a
`NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_ can be
passed for ``src`` to represent padding more efficiently than using a padding
mask. In this case, a `NestedTensor <https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nested.html>`_ will be
returned, and an additional speedup proportional to the fraction of the input that
is padding can be expected.
.. _`FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness`:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135
`TransformerEncoderLayer`由自注意力机制(self-attn)和前馈网络(feedforward network)组成。
**注意**:
有关PyTorch提供的高效构建块来构建您自己的transformer层的深入讨论,请参阅[此教程](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/transformer_building_blocks.html)。
此标准的编码器层基于论文《Attention Is All You Need》:
- Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, 和 Illia Polosukhin。2017年。Attention is all you need. 发表在《神经信息处理系统进展》上,第6000-6010页。用户可以根据需要修改或以不同方式实现。
`TransformerEncoderLayer`可以处理传统的`torch.tensor`输入,或`Nested Tensor`输入。衍生类预计也应接受这两种输入格式。(目前,`TransformerEncoderLayer`并不支持所有输入格式的组合,特别是当`Nested Tensor`处于原型状态时。)
如果您正在实现自定义层,您可以选择从`Module`或`TransformerEncoderLayer`类派生。如果您的自定义层支持`torch.Tensor`和`Nested Tensors`输入,建议将其实现为`TransformerEncoderLayer`的派生类。如果自定义层仅支持`torch.Tensor`输入,请从`Module`类派生。
参数:
- `d_model`:输入中预期的特征数量(必需)。
- `nhead`:多头自注意力模型中的头数(必需)。
- `dim_feedforward`:前馈网络模型的维度(默认为2048)。
- `dropout`:dropout值(默认为0.1)。
- `activation`:中间层的激活函数,可以是字符串("relu"或"gelu")或一个一元可调用对象。默认为`relu`。
- `layer_norm_eps`:层归一化组件中的eps值(默认为1e-5)。
- `batch_first`:如果为`True`,则输入和输出的张量将按(batch, seq, feature)格式提供。默认为`False`(seq, batch, feature)。
- `norm_first`:如果为`True`,则在自注意力和前馈层操作之前应用层归一化。否则,在层之后应用。默认为`False`(之后)。
- `bias`:如果设置为`False`,则`Linear`和`LayerNorm`层将不学习附加偏置。默认为`True`。
示例:
python
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8)
>>> src = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> out = encoder_layer(src)
或者,当`batch_first`为`True`时:
python
>>> encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8, batch_first=True)
>>> src = torch.rand(32, 10, 512)
>>> out = encoder_layer(src)
快速路径:
`forward()`将使用一种特殊的优化实现(在论文`FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness`中描述)如果满足以下所有条件:
- 使用`torch.inference_mode`或`torch.no_grad`禁用autograd,或者没有张量参数需要梯度(`requires_grad`为`False`)。
- 禁用训练模式(使用`.eval()`)。
- `batch_first`为`True`且输入是批处理(即`src.dim() == 3`)。
- 激活函数为以下之一:`"relu"`、`"gelu"`、`torch.functional.relu`或`torch.functional.gelu`。
- 至多传递一个`src_mask`或`src_key_padding_mask`。
- 如果`src`是`NestedTensor`,则不传递`src_mask`或`src_key_padding_mask`。
- 两个`LayerNorm`实例具有一致的`eps`值(除非调用者手动修改了其中一个而没有修改另一个)。
如果优化实现被使用,则可以将`NestedTensor`传递给`src`,它可以比使用填充掩码更有效地表示填充。在这种情况下,返回一个`NestedTensor`,并且可以期望根据输入中填充的比例获得额外的加速。
详细信息请参见[FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135)。
"""
__constants__ = ["norm_first"]
def __init__(
self,
d_model: int,
nhead: int,
dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
dropout: float = 0.1,
activation: Union[str, Callable[[Tensor], Tensor]] = F.relu,
layer_norm_eps: float = 1e-5,
batch_first: bool = False,
norm_first: bool = False,
bias: bool = True,
device=None,
dtype=None,
) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = MultiheadAttention(
d_model,
nhead,
dropout=dropout,
bias=bias,
batch_first=batch_first,
**factory_kwargs,
)
# Implementation of Feedforward model
self.linear1 = Linear(d_model, dim_feedforward, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.dropout = Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = Linear(dim_feedforward, d_model, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.norm_first = norm_first
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model, eps=layer_norm_eps, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model, eps=layer_norm_eps, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.dropout1 = Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout2 = Dropout(dropout)
# Legacy string support for activation function.
if isinstance(activation, str):
activation = _get_activation_fn(activation)
# We can't test self.activation in forward() in TorchScript,
# so stash some information about it instead.
if activation is F.relu or isinstance(activation, torch.nn.ReLU):
self.activation_relu_or_gelu = 1
elif activation is F.gelu or isinstance(activation, torch.nn.GELU):
self.activation_relu_or_gelu = 2
else:
self.activation_relu_or_gelu = 0
self.activation = activation
def __setstate__(self, state):
super().__setstate__(state)
if not hasattr(self, "activation"):
self.activation = F.relu
def forward(
self,
src: Tensor,
src_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
src_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
r"""Pass the input through the encoder layer.
Args:
src: the sequence to the encoder layer (required).
src_mask: the mask for the src sequence (optional).
src_key_padding_mask: the mask for the src keys per batch (optional).
is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as ``src mask``.
Default: ``False``.
Warning:
``is_causal`` provides a hint that ``src_mask`` is the
causal mask. Providing incorrect hints can result in
incorrect execution, including forward and backward
compatibility.
Shape:
see the docs in :class:`~torch.nn.Transformer`.
"""
src_key_padding_mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=src_key_padding_mask,
mask_name="src_key_padding_mask",
other_type=F._none_or_dtype(src_mask),
other_name="src_mask",
target_type=src.dtype,
)
src_mask = F._canonical_mask(
mask=src_mask,
mask_name="src_mask",
other_type=None,
other_name="",
target_type=src.dtype,
check_other=False,
)
is_fastpath_enabled = torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled()
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = ""
if not is_fastpath_enabled:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"torch.backends.mha.get_fastpath_enabled() was not True"
)
elif not src.dim() == 3:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
f"input not batched; expected src.dim() of 3 but got {src.dim()}"
)
elif self.training:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "training is enabled"
elif not self.self_attn.batch_first:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "self_attn.batch_first was not True"
elif self.self_attn.in_proj_bias is None:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "self_attn was passed bias=False"
elif not self.self_attn._qkv_same_embed_dim:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "self_attn._qkv_same_embed_dim was not True"
elif not self.activation_relu_or_gelu:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "activation_relu_or_gelu was not True"
elif not (self.norm1.eps == self.norm2.eps):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "norm1.eps is not equal to norm2.eps"
elif src.is_nested and (
src_key_padding_mask is not None or src_mask is not None
):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "neither src_key_padding_mask nor src_mask are not supported with NestedTensor input"
elif self.self_attn.num_heads % 2 == 1:
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "num_head is odd"
elif torch.is_autocast_enabled():
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "autocast is enabled"
elif any(
len(getattr(m, "_forward_hooks", {}))
+ len(getattr(m, "_forward_pre_hooks", {}))
for m in self.modules()
):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "forward pre-/hooks are attached to the module"
if not why_not_sparsity_fast_path:
tensor_args = (
src,
self.self_attn.in_proj_weight,
self.self_attn.in_proj_bias,
self.self_attn.out_proj.weight,
self.self_attn.out_proj.bias,
self.norm1.weight,
self.norm1.bias,
self.norm2.weight,
self.norm2.bias,
self.linear1.weight,
self.linear1.bias,
self.linear2.weight,
self.linear2.bias,
)
# We have to use list comprehensions below because TorchScript does not support
# generator expressions.
_supported_device_type = [
"cpu",
"cuda",
torch.utils.backend_registration._privateuse1_backend_name,
]
if torch.overrides.has_torch_function(tensor_args):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = "some Tensor argument has_torch_function"
elif not all(
(x.device.type in _supported_device_type) for x in tensor_args
):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"some Tensor argument's device is neither one of "
f"{_supported_device_type}"
)
elif torch.is_grad_enabled() and any(x.requires_grad for x in tensor_args):
why_not_sparsity_fast_path = (
"grad is enabled and at least one of query or the "
"input/output projection weights or biases requires_grad"
)
if not why_not_sparsity_fast_path:
merged_mask, mask_type = self.self_attn.merge_masks(
src_mask, src_key_padding_mask, src
)
return torch._transformer_encoder_layer_fwd(
src,
self.self_attn.embed_dim,
self.self_attn.num_heads,
self.self_attn.in_proj_weight,
self.self_attn.in_proj_bias,
self.self_attn.out_proj.weight,
self.self_attn.out_proj.bias,
self.activation_relu_or_gelu == 2,
self.norm_first,
self.norm1.eps,
self.norm1.weight,
self.norm1.bias,
self.norm2.weight,
self.norm2.bias,
self.linear1.weight,
self.linear1.bias,
self.linear2.weight,
self.linear2.bias,
merged_mask,
mask_type,
)
# see Fig. 1 of https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.04745v1.pdf
x = src
if self.norm_first:
x = x + self._sa_block(
self.norm1(x), src_mask, src_key_padding_mask, is_causal=is_causal
)
x = x + self._ff_block(self.norm2(x))
else:
x = self.norm1(
x
+ self._sa_block(x, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask, is_causal=is_causal)
)
x = self.norm2(x + self._ff_block(x))
return x
# self-attention block
# x 被同时传递给了查询(Query)、键(Key)和值(Value),这在自注意力层中是常见的做法,因为在transformer的encoder部分,查询、键和值通常是相同的(即来自同一输入)
# need_weights=False 表示我们不需要返回注意力权重。
def _sa_block(
self,
x: Tensor,
attn_mask: Optional[Tensor],
key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor],
is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
x = self.self_attn(
x,
x,
x,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
need_weights=False,
is_causal=is_causal,
)[0]
return self.dropout1(x)
# feed forward block
def _ff_block(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.linear2(self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
return self.dropout2(x)
解码器的官方pytorch实现
class TransformerDecoder(Module):
r"""TransformerDecoder is a stack of N decoder layers.
.. note::
See `this tutorial <https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/transformer_building_blocks.html>`_
for an in depth discussion of the performant building blocks PyTorch offers for building your own
transformer layers.
Args:
decoder_layer: an instance of the TransformerDecoderLayer() class (required).
num_layers: the number of sub-decoder-layers in the decoder (required).
norm: the layer normalization component (optional).
Examples::
>>> decoder_layer = nn.TransformerDecoderLayer(d_{model}=512, nhead=8)
>>> transformer_decoder = nn.TransformerDecoder(decoder_layer, num_layers=6)
>>> memory = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> tgt = torch.rand(20, 32, 512)#目标序列(Target Sequence)
>>> out = transformer_decoder(tgt, memory)
"""
__constants__ = ["norm"]
def __init__(
self,
decoder_layer: "TransformerDecoderLayer",
num_layers: int,
norm: Optional[Module] = None,
) -> None:
super().__init__()
torch._C._log_api_usage_once(f"torch.nn.modules.{self.__class__.__name__}")
self.layers = _get_clones(decoder_layer, num_layers)#复制N层解码层
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.norm = norm
def forward(
self,
tgt: Tensor,
memory: Tensor,
tgt_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
memory_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
tgt_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
memory_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
tgt_is_causal: Optional[bool] = None,
memory_is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
r"""Pass the inputs (and mask) through the decoder layer in turn.
Args:
tgt: the sequence to the decoder (required).目标序列(Target Sequence)
memory: the sequence from the last layer of the encoder (required).
tgt_mask: the mask for the tgt sequence (optional).
memory_mask: the mask for the memory sequence (optional).
tgt_key_padding_mask: the mask for the tgt keys per batch (optional).
memory_key_padding_mask: the mask for the memory keys per batch (optional).
tgt_is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as ``tgt mask``.
Default: ``None``; try to detect a causal mask.
Warning:
``tgt_is_causal`` provides a hint that ``tgt_mask`` is
the causal mask. Providing incorrect hints can result in
incorrect execution, including forward and backward
compatibility.
memory_is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as
``memory mask``.
Default: ``False``.
Warning:
``memory_is_causal`` provides a hint that
``memory_mask`` is the causal mask. Providing incorrect
hints can result in incorrect execution, including
forward and backward compatibility.
Shape:
see the docs in :class:`~torch.nn.Transformer`.
"""
output = tgt
seq_len = _get_seq_len(tgt, self.layers[0].self_attn.batch_first)
tgt_is_causal = _detect_is_causal_mask(tgt_mask, tgt_is_causal, seq_len)
for mod in self.layers:
output = mod(
output,
memory,
tgt_mask=tgt_mask,
memory_mask=memory_mask,
tgt_key_padding_mask=tgt_key_padding_mask,
memory_key_padding_mask=memory_key_padding_mask,
tgt_is_causal=tgt_is_causal,
memory_is_causal=memory_is_causal,
)
if self.norm is not None:
output = self.norm(output)
return output
解码器中的每一层TransformerDecoderLayer的pytorch官方实现
class TransformerDecoderLayer(Module):
r"""TransformerDecoderLayer is made up of self-attn, multi-head-attn and feedforward network.
.. note::
See `this tutorial <https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/transformer_building_blocks.html>`_
for an in depth discussion of the performant building blocks PyTorch offers for building your own
transformer layers.
This standard decoder layer is based on the paper "Attention Is All You Need".
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez,
Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. 2017. Attention is all you need. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 6000-6010. Users may modify or implement
in a different way during application.
Args:
d_model: the number of expected features in the input (required).
nhead: the number of heads in the multiheadattention models (required).
dim_feedforward: the dimension of the feedforward network model (default=2048).
dropout: the dropout value (default=0.1).
activation: the activation function of the intermediate layer, can be a string
("relu" or "gelu") or a unary callable. Default: relu
layer_norm_eps: the eps value in layer normalization components (default=1e-5).
batch_first: If ``True``, then the input and output tensors are provided
as (batch, seq, feature). Default: ``False`` (seq, batch, feature).
norm_first: if ``True``, layer norm is done prior to self attention, multihead
attention and feedforward operations, respectively. Otherwise it's done after.
Default: ``False`` (after).
bias: If set to ``False``, ``Linear`` and ``LayerNorm`` layers will not learn an additive
bias. Default: ``True``.
Examples::
>>> decoder_layer = nn.TransformerDecoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8)
>>> memory = torch.rand(10, 32, 512)
>>> tgt = torch.rand(20, 32, 512)
>>> out = decoder_layer(tgt, memory)
Alternatively, when ``batch_first`` is ``True``:
>>> decoder_layer = nn.TransformerDecoderLayer(d_model=512, nhead=8, batch_first=True)
>>> memory = torch.rand(32, 10, 512)
>>> tgt = torch.rand(32, 20, 512)
>>> out = decoder_layer(tgt, memory)
"""
__constants__ = ["norm_first"]
def __init__(
self,
d_model: int,
nhead: int,
dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
dropout: float = 0.1,
activation: Union[str, Callable[[Tensor], Tensor]] = F.relu,
layer_norm_eps: float = 1e-5,
batch_first: bool = False,
norm_first: bool = False,
bias: bool = True,
device=None,
dtype=None,
) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = MultiheadAttention(
d_model,
nhead,
dropout=dropout,
batch_first=batch_first,
bias=bias,
**factory_kwargs,
)
self.multihead_attn = MultiheadAttention(
d_model,
nhead,
dropout=dropout,
batch_first=batch_first,
bias=bias,
**factory_kwargs,
)
# Implementation of Feedforward model
self.linear1 = Linear(d_model, dim_feedforward, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.dropout = Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = Linear(dim_feedforward, d_model, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.norm_first = norm_first
self.norm1 = LayerNorm(d_model, eps=layer_norm_eps, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm(d_model, eps=layer_norm_eps, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.norm3 = LayerNorm(d_model, eps=layer_norm_eps, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.dropout1 = Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout2 = Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout3 = Dropout(dropout)
# Legacy string support for activation function.
if isinstance(activation, str):
self.activation = _get_activation_fn(activation)
else:
self.activation = activation
def __setstate__(self, state):
if "activation" not in state:
state["activation"] = F.relu
super().__setstate__(state)
def forward(
self,
tgt: Tensor,
memory: Tensor,
tgt_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
memory_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
tgt_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
memory_key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor] = None,
tgt_is_causal: bool = False,
memory_is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
r"""Pass the inputs (and mask) through the decoder layer.
Args:
tgt: the sequence to the decoder layer (required).
memory: the sequence from the last layer of the encoder (required).
tgt_mask: the mask for the tgt sequence (optional).
memory_mask: the mask for the memory sequence (optional).
tgt_key_padding_mask: the mask for the tgt keys per batch (optional).
memory_key_padding_mask: the mask for the memory keys per batch (optional).
tgt_is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as ``tgt mask``.
Default: ``False``.
Warning:
``tgt_is_causal`` provides a hint that ``tgt_mask`` is
the causal mask. Providing incorrect hints can result in
incorrect execution, including forward and backward
compatibility.
memory_is_causal: If specified, applies a causal mask as
``memory mask``.
Default: ``False``.
Warning:
``memory_is_causal`` provides a hint that
``memory_mask`` is the causal mask. Providing incorrect
hints can result in incorrect execution, including
forward and backward compatibility.
Shape:
see the docs in :class:`~torch.nn.Transformer`.
"""
# see Fig. 1 of https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.04745v1.pdf
x = tgt
if self.norm_first:
x = x + self._sa_block(
self.norm1(x), tgt_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, tgt_is_causal
)
x = x + self._mha_block(
self.norm2(x),
memory,
memory_mask,
memory_key_padding_mask,
memory_is_causal,
)
x = x + self._ff_block(self.norm3(x))
else:
x = self.norm1(
x + self._sa_block(x, tgt_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, tgt_is_causal)
)
x = self.norm2(
x
+ self._mha_block(
x, memory, memory_mask, memory_key_padding_mask, memory_is_causal
)
)
x = self.norm3(x + self._ff_block(x))
return x
# self-attention block
def _sa_block(
self,
x: Tensor,
attn_mask: Optional[Tensor],
key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor],
is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
x = self.self_attn(
x,
x,
x,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
is_causal=is_causal,
need_weights=False,
)[0]
return self.dropout1(x)
# multihead attention block
def _mha_block(
self,
x: Tensor,
mem: Tensor,
attn_mask: Optional[Tensor],
key_padding_mask: Optional[Tensor],
is_causal: bool = False,
) -> Tensor:
x = self.multihead_attn(
x,
mem,
mem,
attn_mask=attn_mask,
key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask,
is_causal=is_causal,
need_weights=False,
)[0]
return self.dropout2(x)
# feed forward block
def _ff_block(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.linear2(self.dropout(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
return self.dropout3(x)