HiFi-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Efficient and High Fidelity Speech Synthesis
| EN | CN |
解决什么问题
是为了解决声码器不能高效生成高质量保真音频问题
创新
- 引入多周期判别器MPD(MultiPeriodDiscriminator)和多尺度判别器MSD(MultiScaleDiscriminator)来增强GAN的判断能力
- 引入多感受野融合模块MRF(3组leaky_relu+带洞卷积和普通卷积叠加)增大感受野,同时减小了模型体积加速模型训练
解决方法


数据集
数学论证
损失函数
HiFiGAN的损失函数主要包括三块,
- GAN原始的生成对抗损失(GAN Loss): \(\mathcal L_{Adv}( G;D )\)和\(\mathcal L_{Adv}( D;G )\);
- 梅尔频谱损失(Mel-Spectrogram Loss): \(\mathcal L_{Mel}(G)\),将生成音频转换回梅尔频谱之后,计算真实和生成梅尔频谱之间的L1距离;
- 特征匹配损失(Feature Match Loss): \(\mathcal L_{FM} (G; D)\),主要是对比中间卷积层真实和合成样本之间的差异。
\(\mathcal L_{G} = \mathcal L_{Adv}( G;D ) + \lambda_{fm}\mathcal L_{FM}(G;D) + \lambda_{mel}\mathcal L_{Mel}(G)\\ \mathcal L_{D} = \mathcal L_{Adv}( D;G )\) 其中\(\lambda_{fm}=2\),\(\lambda_{mel}=45\)
\[\begin{cases} \mathcal L_{Adv}( G;D ) &=& E_{s}\left [ (D(G(s))-1)^{2} \right ]\\ \mathcal L_{Adv}( D;G ) &=& E_{(x,s)}\left [ (D(x) − 1)^{2} + (D(G(s)))^{2} \right ]\\ \mathcal L_{Mel}(G) &=& E(x,s)[ \left || φ(x) − φ(G(s)) \right ||_{1} ]\\ \mathcal L_{FM} (G; D) &=& E_{(x,s)} [ \sum_{i=1}^{T} \frac{1}{N_{i}}| |D^{i}(x) − D^{i}(G(s))||_{1} ] \end{cases}\]其中
s表示由真实音频转成的mel频谱,x表示真实的音频- \(\phi (x)\)表示使音频转成mel频谱的函数
- T是判别器中的神经网络层数,\(N_{i}\)表示判别器第i层中特征个数, \(D^{i}\)表示判别器第i层中的特征
效果
实验结果证明HiFi-GAN在GPU上可以以比实时速度快1186.8倍的速度生成26169 kHz的语音,在CPU上可以比自回归模型快13.4倍的速度生成语音

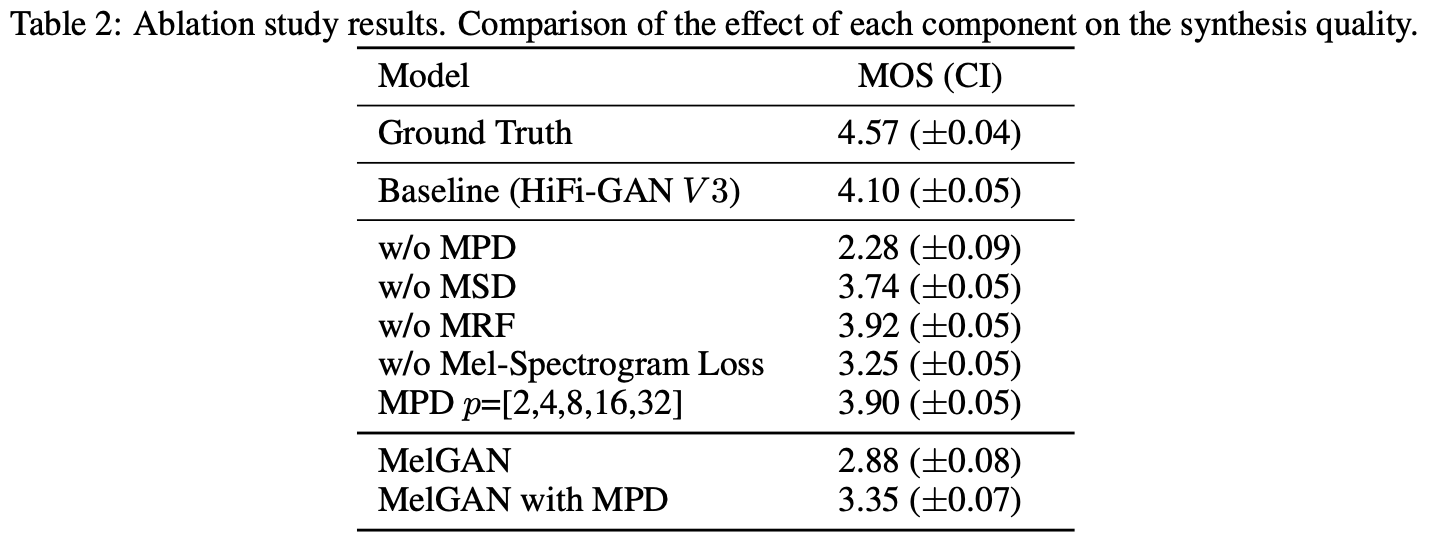
缺点
在TTS中,使用HiFiGAN生成人物音频时会产生电音
Code精读
MPD
周期为素数(2,3,5,7,11),避免判别器重叠
class MultiPeriodDiscriminator(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MultiPeriodDiscriminator, self).__init__()
self.discriminators = nn.ModuleList([
DiscriminatorP(2),
DiscriminatorP(3),
DiscriminatorP(5),
DiscriminatorP(7),
DiscriminatorP(11),
])
def forward(self, y, y_hat):
y_d_rs = []
y_d_gs = []
fmap_rs = []
fmap_gs = []
for i, d in enumerate(self.discriminators):
y_d_r, fmap_r = d(y)
y_d_g, fmap_g = d(y_hat)
y_d_rs.append(y_d_r)
fmap_rs.append(fmap_r)
y_d_gs.append(y_d_g)
fmap_gs.append(fmap_g)
return y_d_rs, y_d_gs, fmap_rs, fmap_gs
class DiscriminatorP(torch.nn.Module):
"""HiFiGAN Periodic Discriminator
Takes every Pth value from the input waveform and applied a stack of convoluations.
Note:
if `period` is 2
`waveform = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ...] --> [1, 3, 5 ... ] --> convs -> score, feat`
Args:
x (Tensor): input waveform.
Returns:
[Tensor]: discriminator scores per sample in the batch.
[List[Tensor]]: list of features from each convolutional layer.
Shapes:
x: [B, 1, T]
"""
def __init__(self, period, kernel_size=5, stride=3, use_spectral_norm=False):
super().__init__()
self.period = period
get_padding = lambda k, d: int((k * d - d) / 2)
norm_f = nn.utils.spectral_norm if use_spectral_norm else nn.utils.weight_norm
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(
[
norm_f(nn.Conv2d(1, 32, (kernel_size, 1), (stride, 1), padding=(get_padding(kernel_size, 1), 0))),
norm_f(nn.Conv2d(32, 128, (kernel_size, 1), (stride, 1), padding=(get_padding(kernel_size, 1), 0))),
norm_f(nn.Conv2d(128, 512, (kernel_size, 1), (stride, 1), padding=(get_padding(kernel_size, 1), 0))),
norm_f(nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, (kernel_size, 1), (stride, 1), padding=(get_padding(kernel_size, 1), 0))),
norm_f(nn.Conv2d(1024, 1024, (kernel_size, 1), 1, padding=(2, 0))),
]
)
self.conv_post = norm_f(nn.Conv2d(1024, 1, (3, 1), 1, padding=(1, 0)))
def forward(self, x):
"""
Args:
x (Tensor): input waveform.
Returns:
[Tensor]: discriminator scores per sample in the batch.
[List[Tensor]]: list of features from each convolutional layer.
Shapes:
x: [B, 1, T]
"""
fmap = []
# 1d to 2d
b, c, t = x.shape
if t % self.period != 0: # pad first
n_pad = self.period - (t % self.period)
x = F.pad(x, (0, n_pad), "reflect")
t = t + n_pad
x = x.view(b, c, t // self.period, self.period)
for l in self.convs:
x = l(x)
x = F.leaky_relu(x, LRELU_SLOPE)
fmap.append(x)
x = self.conv_post(x)
fmap.append(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1, -1)
return x, fmap
MSD
它类似于“MultiscaleMelgandDiscriminator”,但如本文所述,是专门为HiFiGAN量身定制的。 第一个判别器使用了spectral_norm谱归一化,之后两个判别器则是正常的权重归一化weight_norm。谱归一化实际就是在每次更新完可训练参数w之后都除以W的奇异值,以保证整个网络满足利普希茨连续性,使得GAN的训练更稳定。
class MultiScaleDiscriminator(torch.nn.Module):
"""HiFiGAN Multi-Scale Discriminator.
It is similar to `MultiScaleMelganDiscriminator` but specially tailored for HiFiGAN as in the paper.
"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.discriminators = nn.ModuleList(
[
DiscriminatorS(use_spectral_norm=True),
DiscriminatorS(),
DiscriminatorS(),
]
)
self.meanpools = nn.ModuleList([nn.AvgPool1d(4, 2, padding=2), nn.AvgPool1d(4, 2, padding=2)])
def forward(self, y, y_hat):
"""
Args:
x (Tensor): input waveform.
Returns:
List[Tensor]: discriminator scores.
List[List[Tensor]]: list of list of features from each layers of each discriminator.
"""
y_d_rs = []
y_d_gs = []
fmap_rs = []
fmap_gs = []
for i, d in enumerate(self.discriminators):
if i != 0:
y = self.meanpools[i-1](y)
y_hat = self.meanpools[i-1](y_hat)
y_d_r, fmap_r = d(y)
y_d_g, fmap_g = d(y_hat)
y_d_rs.append(y_d_r)
fmap_rs.append(fmap_r)
y_d_gs.append(y_d_g)
fmap_gs.append(fmap_g)
return y_d_rs, y_d_gs, fmap_rs, fmap_gs
其中判别器DiscriminatorS
class DiscriminatorS(torch.nn.Module):
"""HiFiGAN Scale Discriminator.
It is similar to `MelganDiscriminator` but with a specific architecture explained in the paper.
Args:
use_spectral_norm (bool): if `True` swith to spectral norm instead of weight norm.
"""
def __init__(self, use_spectral_norm=False):
super().__init__()
norm_f = nn.utils.spectral_norm if use_spectral_norm else nn.utils.weight_norm
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(
[
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(1, 128, 15, 1, padding=7)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(128, 128, 41, 2, groups=4, padding=20)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(128, 256, 41, 2, groups=16, padding=20)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(256, 512, 41, 4, groups=16, padding=20)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(512, 1024, 41, 4, groups=16, padding=20)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(1024, 1024, 41, 1, groups=16, padding=20)),
norm_f(nn.Conv1d(1024, 1024, 5, 1, padding=2)),
]
)
self.conv_post = norm_f(nn.Conv1d(1024, 1, 3, 1, padding=1))
def forward(self, x):
"""
Args:
x (Tensor): input waveform.
Returns:
Tensor: discriminator scores.
List[Tensor]: list of features from the convolutiona layers.
"""
fmap = []
for l in self.convs:
x = l(x)
x = F.leaky_relu(x, LRELU_SLOPE)
fmap.append(x)
x = self.conv_post(x)
fmap.append(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1, -1)
return x, fmap
总结
HiFiGAN是一个基于对抗博弈的带有一个生成器两个判别器的高效处理音频生成高质量保真的模型,它是目前世界上非常流行的声码器.