Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression
解决了什么问题
为了解决以下l损失函数的问题:
\[\left\{\begin{matrix} \begin{align} IoU &: 无法解决目标框与预测框无交集的情况\\ GIoU &: 收敛速度慢\\ DIoU &: 预测框与目标框不一致 \end{align} \end{matrix}\right.\]在物体检测中, 通常用到的损失函数是IoU(Intersection over Union)和GIoU(generalized IoU), 虽然GIoU补充了IoU在两个box不重叠时候梯度消失无法检测的情况, 但是GIoU还是存在问题(收敛速度慢)
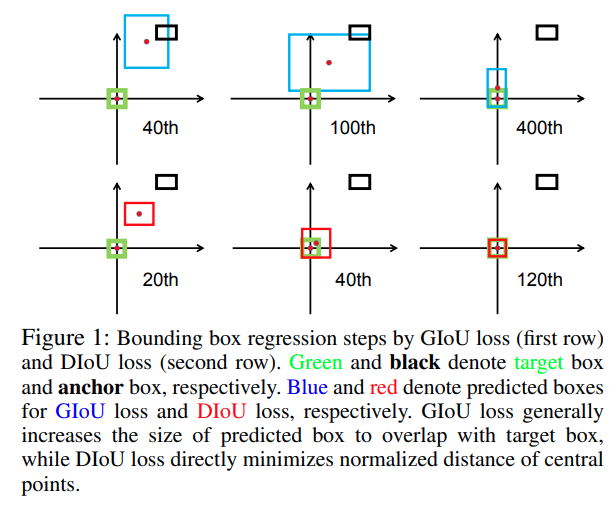
绿色框为真实目标框, 黑色框为首次出现的预测框, 蓝色框是GIoU_Loss预测框, 红色框为DIoU_Loss预测框.
当GIoU与目标框没有交集时, 它必须扩大自己的面积与目标产生交集, 这是导致它收敛慢的主要原因.所以DIoU的提出便是为了解决这个问题. 而DIoU依然存在一个问题, 预测框的大小和目标框不一致. CIoU_Loss的提出便是为了解决这一个问题
方法
\[\begin{eqnarray} \mathcal{L}_{CIoU} & = & 1 - IoU + \frac{\rho^{2}(\textbf{b},\textbf{b}^{gt})}{c^{2}} + \alpha \upsilon\\ v & = & \frac{4}{\pi^{2}} (arctan\frac{w^{gt}}{h^{gt}} - arctan\frac{w}{h})^{2}\\ \alpha & = & \frac{v}{(1-IoU) + v} \\ IoU & = & \frac{\left | B \cap B^{gt} \right | }{\left | B \cup B^{gt} \right |} \\ B^{gt} & = & (x^{gt}, y^{gt}, w^{gt}, h^{gt}) \\ B & = & (x, y, w, h) \end{eqnarray}\]参数:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \(\textbf{b}^{gt}\) | 真实目标框 |
| 2 | \(\textbf{b}\) | 预测框(x,y,w,h)或(x1,y1,x2,y2) |
| 3 | \(\rho\) | 欧氏距离 |
| 4 | \(c\) | 真实框与预测框的最小包围框的对角线长度 |
| 5 | \(\rho(\textbf{b},\textbf{b}^{gt})\) | 真实框与预测框两中心的距离 |

检测算法
数据集
- PASCAL VOC(VOC 2007和VOC 2012)
- MS COCO 2017
效果
Distinguish
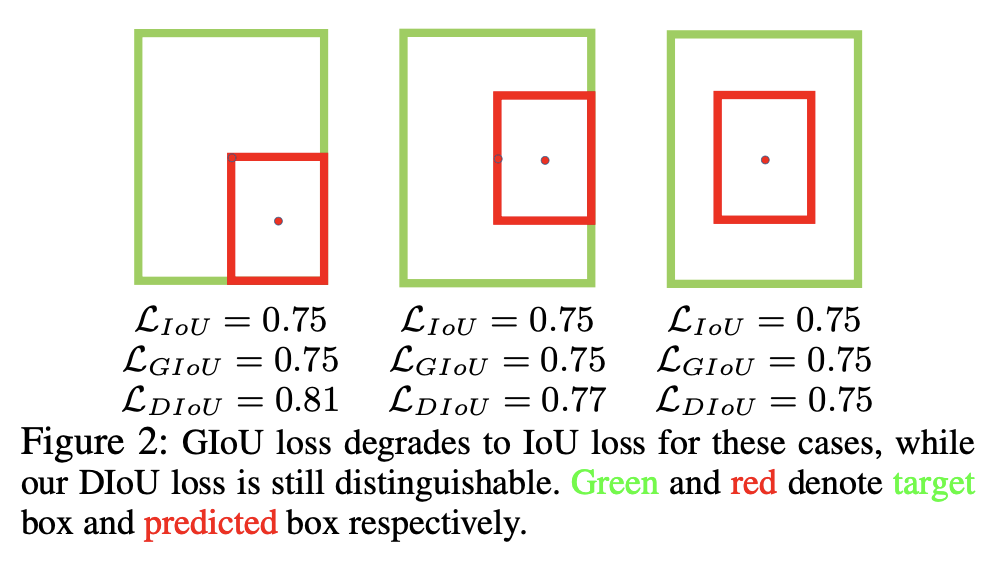
在GIoU和IoU这种情况下相同无法区分时, DIoU依然可以区分
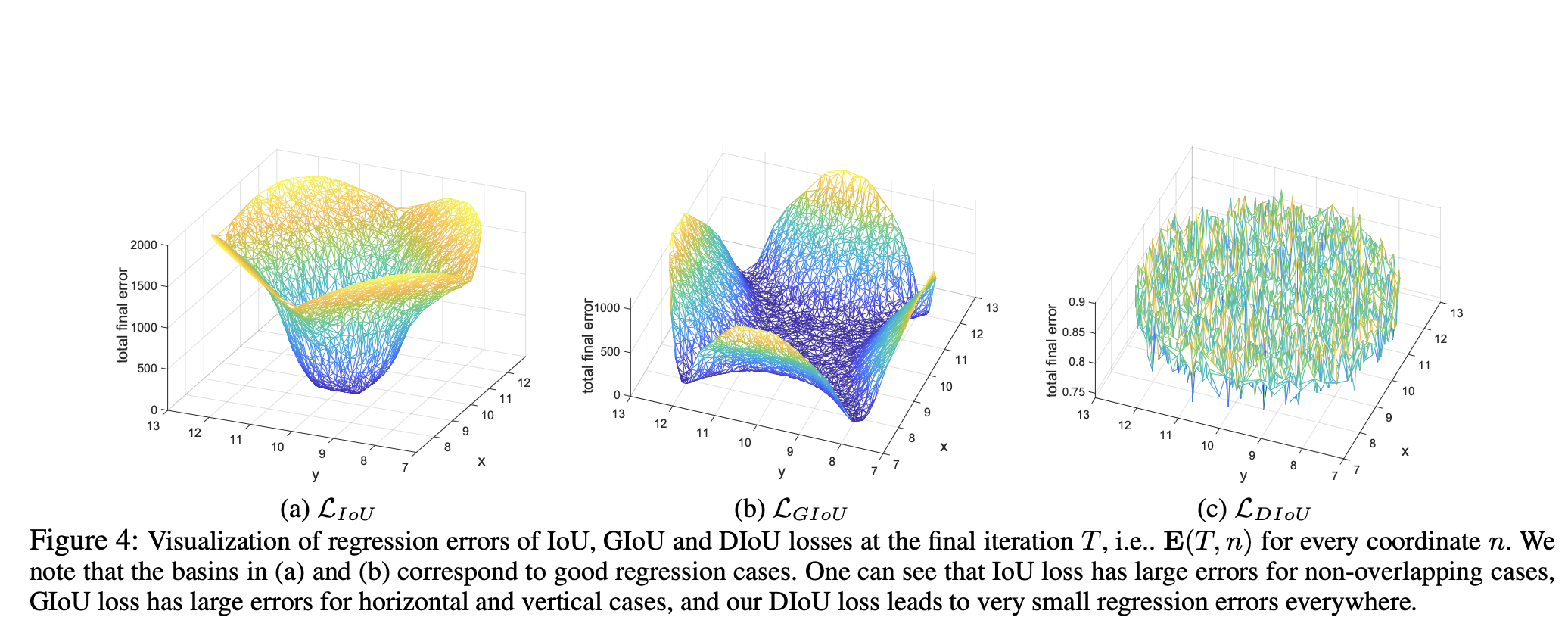
Regression error
在Fig4可以看到, 回归误差E(T,n)在DIoU上是最好的, 所有点都能处在一个低的误差范围

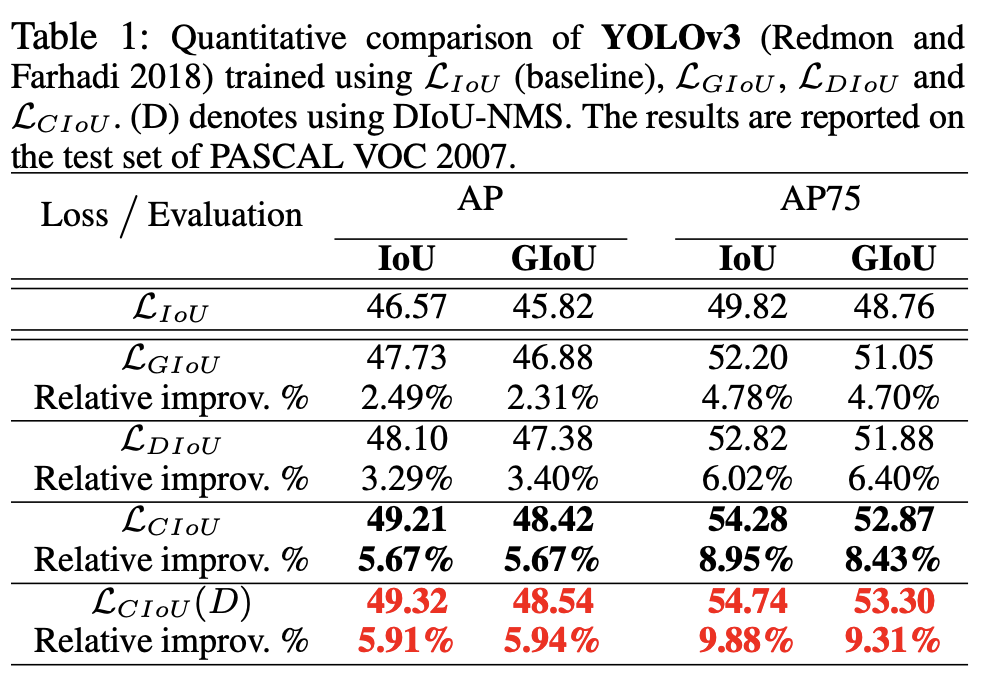
On YOLOv3 with PASCAL VOC 2007
DIoU loss 可以比IoU增加3.29% AP和6.02% AP75
On SSD with PASCAL VOC 2007
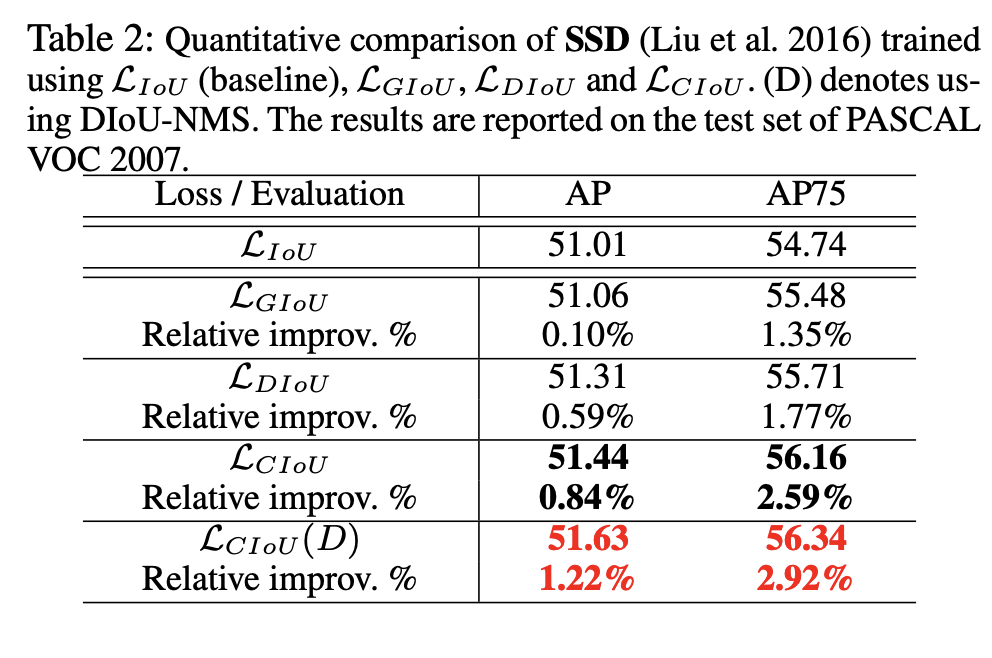
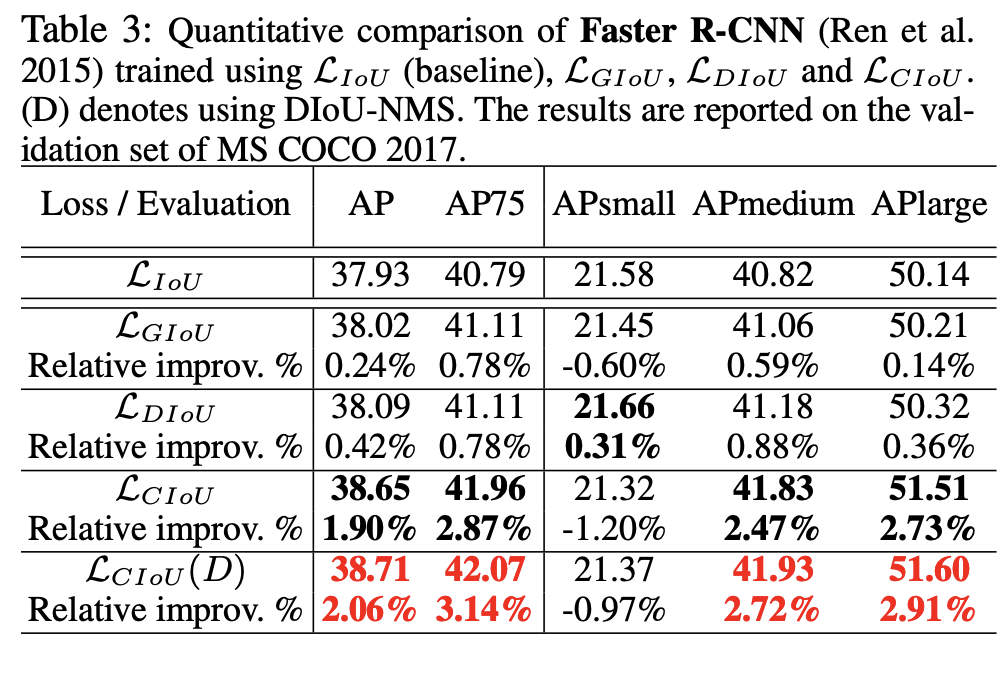
On Faster R-CNN with MS COCO 2017
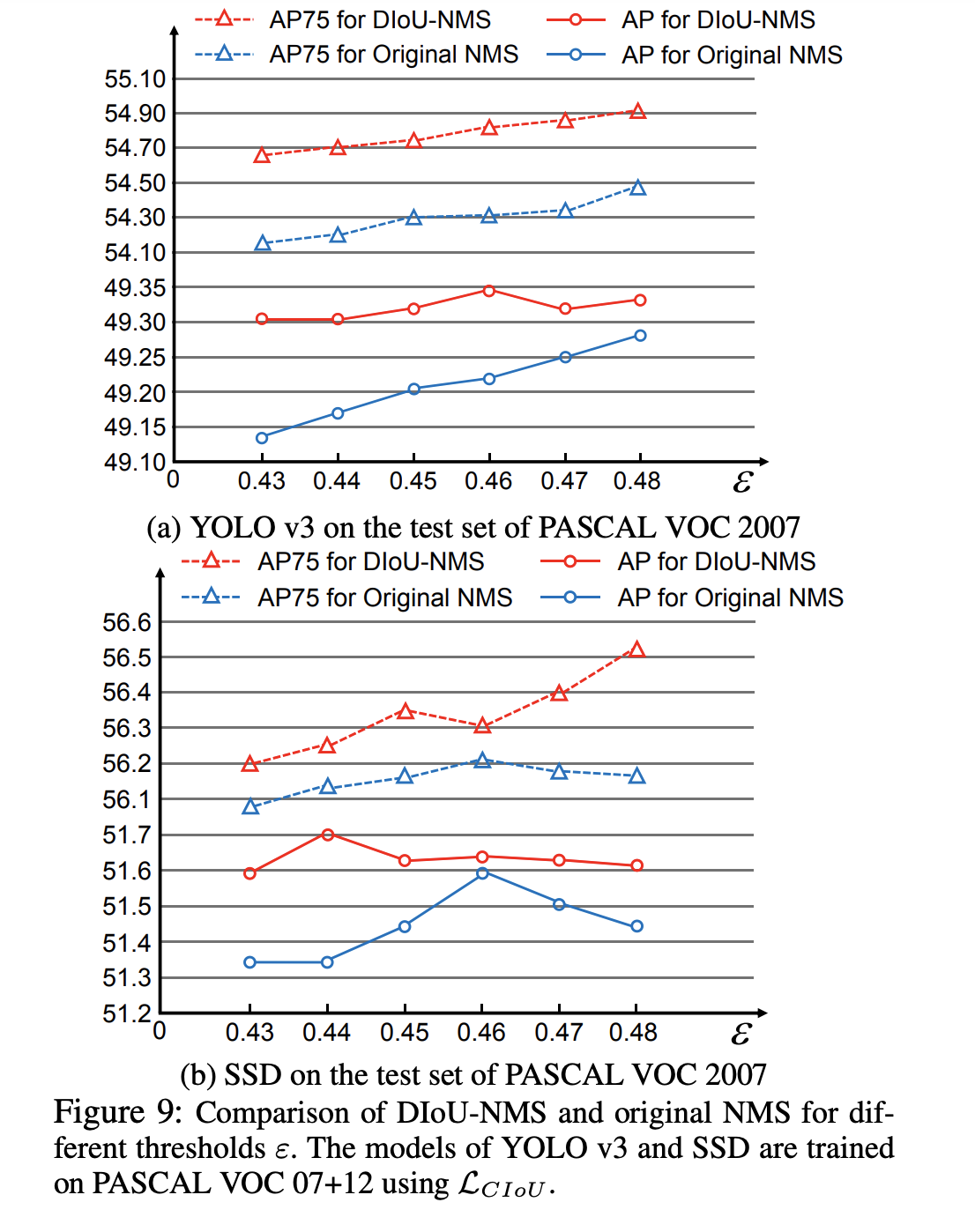
Comparison of DIoU_NMS and original NMS
我们在阈值为[0.43,0.48]范围内比较原NMS和DIoU_NMS。从图9可以看出,DIoU_NMS在各个方面都优于原NMS
所以不需要仔细调整阈值ε也能得到表现比原NMS好的结果。
改进方向
Alpha-IoU: A Family of Power Intersection over Union Losses for Bounding Box Regression
在所有IoU上添加一个α次方,由实验数据可知, \(\alpha \in [2,4]\)效果不错,且\(\alpha = 3\)时最好.
\[\begin{eqnarray}\mathcal{L}_{IoU} &=& 1 − IoU \Rightarrow \mathcal{L}_{\alpha-IoU} = 1 − IoU^{\alpha} \\ \mathcal{L}_{GIoU} &=& 1 − IoU +\frac{|C - B \cup B^{gt}|}{|C|} \Rightarrow \mathcal{L}_{\alpha -GIoU} = 1 − IoU^{\alpha} + (\frac{|C - B \cup B^{gt}|}{|C|})^{\alpha}\\ \mathcal{L}_{DIoU} &=& 1 − IoU +\frac{\rho^{2}(b, bgt)}{c^2} \Rightarrow \mathcal{L}_{\alpha-DIoU} = 1 − IoU^{\alpha} +\frac{\rho^{2\alpha }(b, b^{gt})}{c^{2\alpha} }\\ \mathcal{L}_{CIoU} &=& 1 − IoU +\frac{\rho^{2}(b, bgt)}{c^2}+ \beta v \Rightarrow \mathcal{L}_{\alpha -CIoU} = 1 − IoU^{\alpha} +\frac{\rho^{2\alpha}(b, b^{gt})}{c^{2\alpha}}+ (\beta v)^{\alpha }\end{eqnarray}\]Code精读
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
# Returns the IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.T #转置后形状(4,n)
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else: # transform from xywh to xyxy
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# 交集面积
inter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# 并集面积
w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + eps
w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps
union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps
iou = inter / union
if GIoU or DIoU or CIoU:
cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width最小包围框的宽
ch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height最小包围框的高
if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1
c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared最小包围框的对角线长度的平方
rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 +
(b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center distance squared两个框中心距离的平方
if DIoU:
return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU
elif CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47
v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * torch.pow(torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1), 2)
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU
else: # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf
c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area
return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU
else:
return iou # IoU
- 此代码位于yolov5/utils/metrics.py, box1为预测框, box2为真实目标框.
- 在yolov5/utils/loss.py中, 其x1y1x2y2=False,传入的box参数为(x,y,w,h)
iou = bbox_iou(pbox.T, tbox[i], x1y1x2y2=False, CIoU=True) # iou(prediction, target) lbox += (1.0 - iou).mean() # iou loss - 在物体识别中, 坐标系原点一般为左上角, 整个图像处于第一象限,所以x,y没有负值, clamp(0)只会识别出两个框不相交的情况
扩展
在Yolov11中应用到的其它Loss
| 损失函数 | 使用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 | 论文出处 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VarifocalLoss | 目标检测中的分类任务,特别是处理不平衡数据(如前景和背景样本不平衡)。 | 1. 动态调整样本权重,关注难分类样本。 2. 适用于不平衡数据。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数(如 alpha 和 gamma)。 |
Varifocal Loss: A Dynamic Loss for Dense Object Detection |
| FocalLoss | 目标检测中的分类任务,处理类别不平衡问题。 | 1. 减少易分类样本的损失贡献,关注难分类样本。 2. 缓解类别不平衡问题。 |
1. 需要调整超参数(如 gamma 和 alpha)。2. 对噪声敏感。 |
Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection |
| DFLoss | 目标检测中的边界框回归任务,用于预测边界框的分布。 | 1. 通过分布预测提高边界框回归精度。 2. 适用于密集目标检测。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整 reg_max 参数。 |
Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection |
| BboxLoss | 目标检测中的边界框回归任务,结合 IoU 损失和 DFL 损失。 | 1. 结合 IoU 和 DFL,提高边界框回归精度。 2. 适用于通用目标检测任务。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 IoU 和 DFL 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| RotatedBboxLoss | 旋转目标检测中的边界框回归任务,处理旋转边界框。 | 1. 支持旋转边界框的回归。 2. 适用于旋转目标检测任务。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 IoU 和 DFL 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| KeypointLoss | 关键点检测任务,如人体姿态估计。 | 1. 支持关键点检测任务。 2. 通过欧氏距离计算损失。 |
1. 对关键点标注质量敏感。 2. 需要调整 sigmas 参数。 |
基于 COCO 关键点评估方法,无单独论文。 |
| v8DetectionLoss | YOLOv8 目标检测任务,结合分类、边界框回归和 DFL 损失。 | 1. 综合性强,适用于通用目标检测。 2. 支持多任务学习。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 YOLOv8 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| v8SegmentationLoss | YOLOv8 实例分割任务,结合检测和分割损失。 | 1. 支持实例分割任务。 2. 结合检测和分割损失,提高分割精度。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 YOLOv8 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| v8PoseLoss | YOLOv8 姿态估计任务,结合关键点检测和分类损失。 | 1. 支持姿态估计任务。 2. 结合关键点检测和分类损失,提高姿态估计精度。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 YOLOv8 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| v8ClassificationLoss | YOLOv8 分类任务,用于图像分类。 | 1. 简单高效,适用于分类任务。 2. 使用交叉熵损失,易于实现。 |
1. 仅适用于分类任务,不支持多任务学习。 | 基于交叉熵损失的改进,无单独论文。 |
| v8OBBLoss | YOLOv8 旋转目标检测任务,处理旋转边界框。 | 1. 支持旋转目标检测任务。 2. 结合分类、边界框回归和 DFL 损失。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 YOLOv8 的改进,无单独论文。 |
| E2EDetectLoss | 端到端目标检测任务,结合一对多和一对一检测策略。 | 1. 结合一对多和一对一检测,提高检测精度。 2. 适用于端到端检测任务。 |
1. 计算复杂度较高。 2. 需要调整超参数。 |
基于 YOLOv8 的改进,无单独论文。 |
VarifocalLoss
\(L = \alpha \cdot p^\gamma \cdot (1 - q) + q \cdot \text{BCE}(p, q)\)
class VarifocalLoss(nn.Module):
"""
Varifocal loss by Zhang et al.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.13367.
"""
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize the VarifocalLoss class."""
super().__init__()
@staticmethod
def forward(pred_score, gt_score, label, alpha=0.75, gamma=2.0):
"""Computes varfocal loss."""
weight = alpha * pred_score.sigmoid().pow(gamma) * (1 - label) + gt_score * label
with autocast(enabled=False):
loss = (
(F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_score.float(), gt_score.float(), reduction="none") * weight)
.mean(1)
.sum()
)
return loss
FocalLoss
\(L = -\alpha_t (1 - p_t)^\gamma \log(p_t)\)
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
"""Wraps focal loss around existing loss_fcn(), i.e. criteria = FocalLoss(nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(), gamma=1.5)."""
def __init__(self):
"""Initializer for FocalLoss class with no parameters."""
super().__init__()
@staticmethod
def forward(pred, label, gamma=1.5, alpha=0.25):
"""Calculates and updates confusion matrix for object detection/classification tasks."""
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, label, reduction="none")
# p_t = torch.exp(-loss)
# loss *= self.alpha * (1.000001 - p_t) ** self.gamma # non-zero power for gradient stability
# TF implementation https://github.com/tensorflow/addons/blob/v0.7.1/tensorflow_addons/losses/focal_loss.py
pred_prob = pred.sigmoid() # prob from logits
p_t = label * pred_prob + (1 - label) * (1 - pred_prob)
modulating_factor = (1.0 - p_t) ** gamma
loss *= modulating_factor
if alpha > 0:
alpha_factor = label * alpha + (1 - label) * (1 - alpha)
loss *= alpha_factor
return loss.mean(1).sum()
DFLoss
\(L = \text{CrossEntropy}(p, y_l) \cdot w_l + \text{CrossEntropy}(p, y_r) \cdot w_r\)
class DFLoss(nn.Module):
"""Criterion class for computing DFL losses during training."""
def __init__(self, reg_max=16) -> None:
"""Initialize the DFL module."""
super().__init__()
self.reg_max = reg_max
def __call__(self, pred_dist, target):
"""
Return sum of left and right DFL losses.
Distribution Focal Loss (DFL) proposed in Generalized Focal Loss
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9792391
"""
target = target.clamp_(0, self.reg_max - 1 - 0.01)
tl = target.long() # target left
tr = tl + 1 # target right
wl = tr - target # weight left
wr = 1 - wl # weight right
return (
F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, tl.view(-1), reduction="none").view(tl.shape) * wl
+ F.cross_entropy(pred_dist, tr.view(-1), reduction="none").view(tl.shape) * wr
).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
BboxLoss
\[\begin{align} \text{FG 表示所有正样本的集合} \\ w_i &= \sum_j \text{target_scores}_{ij} \\ S &= \text{target_scores_sum 是正样本目标得分的总和} \\ \text{IoU 损失:} L_{iou} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \text{FG}} w_i \cdot \left(1 - \text{IoU}(\hat{b}_i, b_i)\right) \quad \text{if reg_max} \le 1 \\ \text{DFL 损失:} L_{dfl} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \text{FG}} w_i \cdot \text{DFLoss}(\text{pred_dist}_i, t_i) \quad \text{if reg_max} > 1 \end{align}\]class BboxLoss(nn.Module):
"""Criterion class for computing training losses during training."""
def __init__(self, reg_max=16):
"""Initialize the BboxLoss module with regularization maximum and DFL settings."""
super().__init__()
self.dfl_loss = DFLoss(reg_max) if reg_max > 1 else None
def forward(self, pred_dist, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask):
"""IoU loss."""
weight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1)
iou = bbox_iou(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask], xywh=False, CIoU=True)
loss_iou = ((1.0 - iou) * weight).sum() / target_scores_sum
# DFL loss
if self.dfl_loss:
target_ltrb = bbox2dist(anchor_points, target_bboxes, self.dfl_loss.reg_max - 1)
loss_dfl = self.dfl_loss(pred_dist[fg_mask].view(-1, self.dfl_loss.reg_max), target_ltrb[fg_mask]) * weight
loss_dfl = loss_dfl.sum() / target_scores_sum
else:
loss_dfl = torch.tensor(0.0).to(pred_dist.device)
return loss_iou, loss_dfl
RotatedBboxLoss
\[\begin{align} \mathcal{F} \text{ 表示所有正样本的集合} \\ w_i &= \sum_j \text{target_scores}_{ij} \\ S &= \sum_{i \in \mathcal{F}} w_i \text{ 是正样本目标得分的总和, 归一化因子} \\ L_{iou} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{F}} w_i \cdot \left(1 - \text{probiou}(\hat{b}_i, b_i)\right) \quad \text{if reg_max} \le 1 \\ L_{dfl} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{F}} w_i \cdot \text{DFLoss}(\text{pred_dist}_i, t_i) \quad \text{if reg_max} > 1 \end{align}\]class RotatedBboxLoss(BboxLoss):
"""Criterion class for computing training losses during training."""
def __init__(self, reg_max):
"""Initialize the BboxLoss module with regularization maximum and DFL settings."""
super().__init__(reg_max)
def forward(self, pred_dist, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask):
"""IoU loss."""
weight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1)
iou = probiou(pred_bboxes[fg_mask], target_bboxes[fg_mask])
loss_iou = ((1.0 - iou) * weight).sum() / target_scores_sum
# DFL loss
if self.dfl_loss:
target_ltrb = bbox2dist(anchor_points, xywh2xyxy(target_bboxes[..., :4]), self.dfl_loss.reg_max - 1)
loss_dfl = self.dfl_loss(pred_dist[fg_mask].view(-1, self.dfl_loss.reg_max), target_ltrb[fg_mask]) * weight
loss_dfl = loss_dfl.sum() / target_scores_sum
else:
loss_dfl = torch.tensor(0.0).to(pred_dist.device)
return loss_iou, loss_dfl
其中probiou是计算基于高斯分布的 IoU,它使用协方差矩阵和Bhattacharyya距离衡量 OBB 之间的不确定性差异。
- 输入 OBB 数据:函数接收两个形状为
(N,5)的张量,表示N个旋转边界框,格式为(x, y, w, h, r)。 - 计算中心坐标:拆分输入 OBB,获取
(x, y)作为中心坐标。 - 计算协方差矩阵:
_get_covariance_matrix(obb)计算每个 OBB 的协方差矩阵的参数(a, b, c),表示高斯分布的形状。 \(\begin{aligned}a_i &= \frac{w_i^2}{12}\cos^2 r_i + \frac{h_i^2}{12}\sin^2 r_i, \\ b_i &= \frac{w_i^2}{12}\sin^2 r_i + \frac{h_i^2}{12}\cos^2 r_i, \\ c_i &= \left(\frac{w_i^2}{12} - \frac{h_i^2}{12}\right)\cos r_i\,\sin r_i, \end{aligned}\)
- 计算 Bhattacharyya 距离(BD):
T1计算中心点分布差异;T2计算相关性项;T3计算协方差矩阵的相似性项;BD = T1 + T2 + T3,限制 BD 取值范围以保持数值稳定性。 \(\begin{cases} t_1 = \frac{1}{4} \cdot \frac{(a_1+a_2)(y_1-y_2)^2 + (b_1+b_2)(x_1-x_2)^2}{(a_1+a_2)(b_1+b_2) - (c_1+c_2)^2 + \epsilon}\\ t_2 = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{(c_1+c_2)(x_2-x_1)(y_1-y_2)}{(a_1+a_2)(b_1+b_2) - (c_1+c_2)^2 + \epsilon}\\ t_3 = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \ln\!\left(\frac{(a_1+a_2)(b_1+b_2) - (c_1+c_2)^2}{4 \sqrt{\max\{0,\,a_1b_1-c_1^2\}\cdot\max\{0,\,a_2b_2-c_2^2\}} + \epsilon} + \epsilon\right) \end{cases}\)
- 计算 Hellinger 距离(HD):
HD = sqrt(1 - exp(-BD)),用于转换 BD 到相似度衡量。- Hellinger 距离的离散概率分布计算公式:\(H(P,Q)=\sqrt[]{\frac{1}{2} \sum_{i}^{}(\sqrt[]{p_i}-\sqrt[]{q_i} })^2\)
- 计算最终的 Probiou:
IoU = 1 - HD,得到 Probiou 评分。
- 可选 CIoU 计算:
- 计算宽高比的影响
v; - 计算 alpha 作为权重调整 IoU;
return iou - v * alpha返回 CIoU 结果。
- 计算宽高比的影响
def probiou(obb1, obb2, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7):
"""
计算两个旋转边界框(OBB)的概率 IoU(Probiou)。
该方法基于论文 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.06072v1.pdf 实现。
它采用 Bhattacharyya 距离(BD)和 Hellinger 距离(HD)计算两个 OBB 的相似度。
Args:
obb1 (torch.Tensor): 真实 OBBs, 形状 (N, 5),格式为 (x, y, w, h, r)。
obb2 (torch.Tensor): 预测 OBBs, 形状 (N, 5),格式为 (x, y, w, h, r)。
CIoU (bool, optional): 是否计算 CIoU,默认为 False。
eps (float, optional): 避免除零错误的小数值,默认为 1e-7。
Returns:
torch.Tensor: 计算得到的 OBB 相似度分数,形状 (N, )。
备注:
OBB 格式: [中心 x, 中心 y, 宽度 w, 高度 h, 旋转角度 r]。
若 CIoU=True,则返回 CIoU 而不是普通的 Probiou。
"""
# 提取中心坐标
x1, y1 = obb1[..., :2].split(1, dim=-1) # 真实框中心
x2, y2 = obb2[..., :2].split(1, dim=-1) # 预测框中心
# 计算两个 OBB 的协方差矩阵
a1, b1, c1 = _get_covariance_matrix(obb1) # OBB1 的协方差矩阵参数
a2, b2, c2 = _get_covariance_matrix(obb2) # OBB2 的协方差矩阵参数
# 计算 Bhattacharyya 距离的三部分
# T1: 计算两个边界框的中心点分布差异
t1 = (
((a1 + a2) * (y1 - y2).pow(2) + (b1 + b2) * (x1 - x2).pow(2)) /
((a1 + a2) * (b1 + b2) - (c1 + c2).pow(2) + eps)
) * 0.25
# T2: 计算相关性项
t2 = (
((c1 + c2) * (x2 - x1) * (y1 - y2)) /
((a1 + a2) * (b1 + b2) - (c1 + c2).pow(2) + eps)
) * 0.5
# T3: 计算协方差矩阵之间的相似度
t3 = (
((a1 + a2) * (b1 + b2) - (c1 + c2).pow(2)) /
(4 * ((a1 * b1 - c1.pow(2)).clamp_(0) * (a2 * b2 - c2.pow(2)).clamp_(0)).sqrt() + eps)
+ eps
).log() * 0.5
# 计算 Bhattacharyya 距离(BD)
bd = (t1 + t2 + t3).clamp(eps, 100.0) # 限制 BD 取值范围,避免过大影响计算
# 计算 Hellinger 距离(HD)
hd = (1.0 - (-bd).exp() + eps).sqrt() # HD 通过 BD 指数化处理
# 计算最终的 Probiou 值
iou = 1 - hd # Probiou 计算公式
# 若启用 CIoU,则加入长宽比因素
if CIoU:
# 提取宽高
w1, h1 = obb1[..., 2:4].split(1, dim=-1)
w2, h2 = obb2[..., 2:4].split(1, dim=-1)
# 计算宽高比的影响
v = (4 / math.pi**2) * ((w2 / h2).atan() - (w1 / h1).atan()).pow(2)
# 计算 alpha 权重
with torch.no_grad():
alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))
# 计算最终 CIoU 值
return iou - v * alpha
return iou
KeypointLoss
\[\begin{cases} d_{i,k} &= \left(x_{i,k}^{\text{pred}} - x_{i,k}^{\text{gt}}\right)^2 + \left(y_{i,k}^{\text{pred}} - y_{i,k}^{\text{gt}}\right)^2, \text{对于每个样本 i 中的每个关键点 k} \\ e_{i,k} &= \frac{d_{i,k}}{8\,\sigma_k^2 \cdot (A_i + \epsilon)}, \quad A_i = \text{目标区域面积}, \sigma_k = \text{标准差} \\ l_{i,k} &= 1 - e^\left(-e_{i,k}\right) \\ \lambda_i &= \frac{K}{\sum_{k=1}^{K} m_{i,k} + \epsilon}, \quad K = \text{关键点总数(即 kpt_mask.shape[1])}, m_{i,k} = \text{关键点掩码,若该关键点有效则为 1,否则为 0} \\ L &= \frac{1}{N \times K} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \lambda_i \sum_{k=1}^{K} m_{i,k} \cdot l_{i,k}, \quad \text{N 是批次中的样本数} \end{cases}\]class KeypointLoss(nn.Module):
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __init__(self, sigmas) -> None:
"""Initialize the KeypointLoss class."""
super().__init__()
self.sigmas = sigmas
def forward(self, pred_kpts, gt_kpts, kpt_mask, area):
"""Calculates keypoint loss factor and Euclidean distance loss for predicted and actual keypoints."""
d = (pred_kpts[..., 0] - gt_kpts[..., 0]).pow(2) + (pred_kpts[..., 1] - gt_kpts[..., 1]).pow(2)
kpt_loss_factor = kpt_mask.shape[1] / (torch.sum(kpt_mask != 0, dim=1) + 1e-9)
# e = d / (2 * (area * self.sigmas) ** 2 + 1e-9) # from formula
e = d / ((2 * self.sigmas).pow(2) * (area + 1e-9) * 2) # from cocoeval
return (kpt_loss_factor.view(-1, 1) * ((1 - torch.exp(-e)) * kpt_mask)).mean()
v8DetectionLoss
\[L = L_{cls} + L_{box} + L_{dfl}\]class v8DetectionLoss:
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __init__(self, model, tal_topk=10): # model must be de-paralleled
"""Initializes v8DetectionLoss with the model, defining model-related properties and BCE loss function."""
device = next(model.parameters()).device # get model device
h = model.args # hyperparameters
m = model.model[-1] # Detect() module
self.bce = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction="none")
self.hyp = h
self.stride = m.stride # model strides
self.nc = m.nc # number of classes
self.no = m.nc + m.reg_max * 4
self.reg_max = m.reg_max
self.device = device
self.use_dfl = m.reg_max > 1
self.assigner = TaskAlignedAssigner(topk=tal_topk, num_classes=self.nc, alpha=0.5, beta=6.0)
self.bbox_loss = BboxLoss(m.reg_max).to(device)
self.proj = torch.arange(m.reg_max, dtype=torch.float, device=device)
def preprocess(self, targets, batch_size, scale_tensor):
"""Preprocesses the target counts and matches with the input batch size to output a tensor."""
nl, ne = targets.shape
if nl == 0:
out = torch.zeros(batch_size, 0, ne - 1, device=self.device)
else:
i = targets[:, 0] # image index
_, counts = i.unique(return_counts=True)
counts = counts.to(dtype=torch.int32)
out = torch.zeros(batch_size, counts.max(), ne - 1, device=self.device)
for j in range(batch_size):
matches = i == j
if n := matches.sum():
out[j, :n] = targets[matches, 1:]
out[..., 1:5] = xywh2xyxy(out[..., 1:5].mul_(scale_tensor))
return out
def bbox_decode(self, anchor_points, pred_dist):
"""Decode predicted object bounding box coordinates from anchor points and distribution."""
if self.use_dfl:
b, a, c = pred_dist.shape # batch, anchors, channels
pred_dist = pred_dist.view(b, a, 4, c // 4).softmax(3).matmul(self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype))
# pred_dist = pred_dist.view(b, a, c // 4, 4).transpose(2,3).softmax(3).matmul(self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype))
# pred_dist = (pred_dist.view(b, a, c // 4, 4).softmax(2) * self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype).view(1, 1, -1, 1)).sum(2)
return dist2bbox(pred_dist, anchor_points, xywh=False)
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Calculate the sum of the loss for box, cls and dfl multiplied by batch size."""
loss = torch.zeros(3, device=self.device) # box, cls, dfl
feats = preds[1] if isinstance(preds, tuple) else preds
pred_distri, pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split(
(self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1
)
pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
dtype = pred_scores.dtype
batch_size = pred_scores.shape[0]
imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)
anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)
# Targets
targets = torch.cat((batch["batch_idx"].view(-1, 1), batch["cls"].view(-1, 1), batch["bboxes"]), 1)
targets = self.preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]])
gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 4), 2) # cls, xyxy
mask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0.0)
# Pboxes
pred_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri) # xyxy, (b, h*w, 4)
# dfl_conf = pred_distri.view(batch_size, -1, 4, self.reg_max).detach().softmax(-1)
# dfl_conf = (dfl_conf.amax(-1).mean(-1) + dfl_conf.amax(-1).amin(-1)) / 2
_, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, _ = self.assigner(
# pred_scores.detach().sigmoid() * 0.8 + dfl_conf.unsqueeze(-1) * 0.2,
pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(),
(pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor).type(gt_bboxes.dtype),
anchor_points * stride_tensor,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
mask_gt,
)
target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)
# Cls loss
# loss[1] = self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL way
loss[1] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCE
# Bbox loss
if fg_mask.sum():
target_bboxes /= stride_tensor
loss[0], loss[2] = self.bbox_loss(
pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask
)
loss[0] *= self.hyp.box # box gain
loss[1] *= self.hyp.cls # cls gain
loss[2] *= self.hyp.dfl # dfl gain
return loss.sum() * batch_size, loss.detach() # loss(box, cls, dfl)
v8SegmentationLoss
\[L = L_{box} + L_{cls} + L_{dfl} + L_{mask}\]class v8SegmentationLoss(v8DetectionLoss):
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __init__(self, model): # model must be de-paralleled
"""Initializes the v8SegmentationLoss class, taking a de-paralleled model as argument."""
super().__init__(model)
self.overlap = model.args.overlap_mask
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Calculate and return the loss for the YOLO model."""
loss = torch.zeros(4, device=self.device) # box, cls, dfl
feats, pred_masks, proto = preds if len(preds) == 3 else preds[1]
batch_size, _, mask_h, mask_w = proto.shape # batch size, number of masks, mask height, mask width
pred_distri, pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split(
(self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1
)
# B, grids, ..
pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_masks = pred_masks.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
dtype = pred_scores.dtype
imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)
anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)
# Targets
try:
batch_idx = batch["batch_idx"].view(-1, 1)
targets = torch.cat((batch_idx, batch["cls"].view(-1, 1), batch["bboxes"]), 1)
targets = self.preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]])
gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 4), 2) # cls, xyxy
mask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0.0)
except RuntimeError as e:
raise TypeError(
"ERROR ❌ segment dataset incorrectly formatted or not a segment dataset.\n"
"This error can occur when incorrectly training a 'segment' model on a 'detect' dataset, "
"i.e. 'yolo train model=yolo11n-seg.pt data=coco8.yaml'.\nVerify your dataset is a "
"correctly formatted 'segment' dataset using 'data=coco8-seg.yaml' "
"as an example.\nSee https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/segment/ for help."
) from e
# Pboxes
pred_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri) # xyxy, (b, h*w, 4)
_, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, target_gt_idx = self.assigner(
pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(),
(pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor).type(gt_bboxes.dtype),
anchor_points * stride_tensor,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
mask_gt,
)
target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)
# Cls loss
# loss[1] = self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL way
loss[2] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCE
if fg_mask.sum():
# Bbox loss
loss[0], loss[3] = self.bbox_loss(
pred_distri,
pred_bboxes,
anchor_points,
target_bboxes / stride_tensor,
target_scores,
target_scores_sum,
fg_mask,
)
# Masks loss
masks = batch["masks"].to(self.device).float()
if tuple(masks.shape[-2:]) != (mask_h, mask_w): # downsample
masks = F.interpolate(masks[None], (mask_h, mask_w), mode="nearest")[0]
loss[1] = self.calculate_segmentation_loss(
fg_mask, masks, target_gt_idx, target_bboxes, batch_idx, proto, pred_masks, imgsz, self.overlap
)
# WARNING: lines below prevent Multi-GPU DDP 'unused gradient' PyTorch errors, do not remove
else:
loss[1] += (proto * 0).sum() + (pred_masks * 0).sum() # inf sums may lead to nan loss
loss[0] *= self.hyp.box # box gain
loss[1] *= self.hyp.box # seg gain
loss[2] *= self.hyp.cls # cls gain
loss[3] *= self.hyp.dfl # dfl gain
return loss.sum() * batch_size, loss.detach() # loss(box, cls, dfl)
@staticmethod
def single_mask_loss(
gt_mask: torch.Tensor, pred: torch.Tensor, proto: torch.Tensor, xyxy: torch.Tensor, area: torch.Tensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Compute the instance segmentation loss for a single image.
Args:
gt_mask (torch.Tensor): Ground truth mask of shape (n, H, W), where n is the number of objects.
pred (torch.Tensor): Predicted mask coefficients of shape (n, 32).
proto (torch.Tensor): Prototype masks of shape (32, H, W).
xyxy (torch.Tensor): Ground truth bounding boxes in xyxy format, normalized to [0, 1], of shape (n, 4).
area (torch.Tensor): Area of each ground truth bounding box of shape (n,).
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The calculated mask loss for a single image.
Notes:
The function uses the equation pred_mask = torch.einsum('in,nhw->ihw', pred, proto) to produce the
predicted masks from the prototype masks and predicted mask coefficients.
"""
pred_mask = torch.einsum("in,nhw->ihw", pred, proto) # (n, 32) @ (32, 80, 80) -> (n, 80, 80)
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_mask, gt_mask, reduction="none")
return (crop_mask(loss, xyxy).mean(dim=(1, 2)) / area).sum()
def calculate_segmentation_loss(
self,
fg_mask: torch.Tensor,
masks: torch.Tensor,
target_gt_idx: torch.Tensor,
target_bboxes: torch.Tensor,
batch_idx: torch.Tensor,
proto: torch.Tensor,
pred_masks: torch.Tensor,
imgsz: torch.Tensor,
overlap: bool,
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Calculate the loss for instance segmentation.
Args:
fg_mask (torch.Tensor): A binary tensor of shape (BS, N_anchors) indicating which anchors are positive.
masks (torch.Tensor): Ground truth masks of shape (BS, H, W) if `overlap` is False, otherwise (BS, ?, H, W).
target_gt_idx (torch.Tensor): Indexes of ground truth objects for each anchor of shape (BS, N_anchors).
target_bboxes (torch.Tensor): Ground truth bounding boxes for each anchor of shape (BS, N_anchors, 4).
batch_idx (torch.Tensor): Batch indices of shape (N_labels_in_batch, 1).
proto (torch.Tensor): Prototype masks of shape (BS, 32, H, W).
pred_masks (torch.Tensor): Predicted masks for each anchor of shape (BS, N_anchors, 32).
imgsz (torch.Tensor): Size of the input image as a tensor of shape (2), i.e., (H, W).
overlap (bool): Whether the masks in `masks` tensor overlap.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The calculated loss for instance segmentation.
Notes:
The batch loss can be computed for improved speed at higher memory usage.
For example, pred_mask can be computed as follows:
pred_mask = torch.einsum('in,nhw->ihw', pred, proto) # (i, 32) @ (32, 160, 160) -> (i, 160, 160)
"""
_, _, mask_h, mask_w = proto.shape
loss = 0
# Normalize to 0-1
target_bboxes_normalized = target_bboxes / imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]]
# Areas of target bboxes
marea = xyxy2xywh(target_bboxes_normalized)[..., 2:].prod(2)
# Normalize to mask size
mxyxy = target_bboxes_normalized * torch.tensor([mask_w, mask_h, mask_w, mask_h], device=proto.device)
for i, single_i in enumerate(zip(fg_mask, target_gt_idx, pred_masks, proto, mxyxy, marea, masks)):
fg_mask_i, target_gt_idx_i, pred_masks_i, proto_i, mxyxy_i, marea_i, masks_i = single_i
if fg_mask_i.any():
mask_idx = target_gt_idx_i[fg_mask_i]
if overlap:
gt_mask = masks_i == (mask_idx + 1).view(-1, 1, 1)
gt_mask = gt_mask.float()
else:
gt_mask = masks[batch_idx.view(-1) == i][mask_idx]
loss += self.single_mask_loss(
gt_mask, pred_masks_i[fg_mask_i], proto_i, mxyxy_i[fg_mask_i], marea_i[fg_mask_i]
)
# WARNING: lines below prevents Multi-GPU DDP 'unused gradient' PyTorch errors, do not remove
else:
loss += (proto * 0).sum() + (pred_masks * 0).sum() # inf sums may lead to nan loss
return loss / fg_mask.sum()
v8PoseLoss
\[\begin{cases} L_{\text{box}} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{F}} w_i \Bigl[1 - \text{IoU}(\hat{b}_i, b_i)\Bigr] \\ L_{\text{dfl}} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i \in \mathcal{F}} w_i \cdot \text{DFLoss}(p_i, t_i) \\ L_{\text{cls}} &= \frac{1}{S} \sum_{i} \text{BCE}(p^{cls}_i, q_i) \\ L_{\text{kpt}} &= \frac{1}{N \cdot K} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \lambda_i \sum_{k=1}^{K} m_{i,k} \left[1 - \exp\Bigl(-\frac{d_{i,k}}{8\,\sigma_k^2\,(A_i + \epsilon)}\Bigr)\right] \\ L_{\text{kobj}} &= \text{BCE_pose}\Bigl(p^{\text{kobj}}_{i,k}, m_{i,k}\Bigr) \\ \mathcal{L} &= N \cdot \Bigl[ \lambda_{\text{box}} L_{\text{box}} + \lambda_{\text{pose}} L_{\text{kpt}} + \lambda_{\text{kobj}} L_{\text{kobj}} + \lambda_{\text{cls}} L_{\text{cls}} + \lambda_{\text{dfl}} L_{\text{dfl}} \Bigr], \quad \lambda_{\text{box}} = \text{self.hyp.box} \end{cases}\]class v8PoseLoss(v8DetectionLoss):
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __init__(self, model): # model must be de-paralleled
"""Initializes v8PoseLoss with model, sets keypoint variables and declares a keypoint loss instance."""
super().__init__(model)
self.kpt_shape = model.model[-1].kpt_shape
self.bce_pose = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
is_pose = self.kpt_shape == [17, 3]
nkpt = self.kpt_shape[0] # number of keypoints
sigmas = torch.from_numpy(OKS_SIGMA).to(self.device) if is_pose else torch.ones(nkpt, device=self.device) / nkpt
self.keypoint_loss = KeypointLoss(sigmas=sigmas)
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Calculate the total loss and detach it."""
loss = torch.zeros(5, device=self.device) # box, cls, dfl, kpt_location, kpt_visibility
feats, pred_kpts = preds if isinstance(preds[0], list) else preds[1]
pred_distri, pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split(
(self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1
)
# B, grids, ..
pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_kpts = pred_kpts.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
dtype = pred_scores.dtype
imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)
anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)
# Targets
batch_size = pred_scores.shape[0]
batch_idx = batch["batch_idx"].view(-1, 1)
targets = torch.cat((batch_idx, batch["cls"].view(-1, 1), batch["bboxes"]), 1)
targets = self.preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]])
gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 4), 2) # cls, xyxy
mask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0.0)
# Pboxes
pred_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri) # xyxy, (b, h*w, 4)
pred_kpts = self.kpts_decode(anchor_points, pred_kpts.view(batch_size, -1, *self.kpt_shape)) # (b, h*w, 17, 3)
_, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, target_gt_idx = self.assigner(
pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(),
(pred_bboxes.detach() * stride_tensor).type(gt_bboxes.dtype),
anchor_points * stride_tensor,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
mask_gt,
)
target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)
# Cls loss
# loss[1] = self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL way
loss[3] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCE
# Bbox loss
if fg_mask.sum():
target_bboxes /= stride_tensor
loss[0], loss[4] = self.bbox_loss(
pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask
)
keypoints = batch["keypoints"].to(self.device).float().clone()
keypoints[..., 0] *= imgsz[1]
keypoints[..., 1] *= imgsz[0]
loss[1], loss[2] = self.calculate_keypoints_loss(
fg_mask, target_gt_idx, keypoints, batch_idx, stride_tensor, target_bboxes, pred_kpts
)
loss[0] *= self.hyp.box # box gain
loss[1] *= self.hyp.pose # pose gain
loss[2] *= self.hyp.kobj # kobj gain
loss[3] *= self.hyp.cls # cls gain
loss[4] *= self.hyp.dfl # dfl gain
return loss.sum() * batch_size, loss.detach() # loss(box, cls, dfl)
@staticmethod
def kpts_decode(anchor_points, pred_kpts):
"""Decodes predicted keypoints to image coordinates."""
y = pred_kpts.clone()
y[..., :2] *= 2.0
y[..., 0] += anchor_points[:, [0]] - 0.5
y[..., 1] += anchor_points[:, [1]] - 0.5
return y
def calculate_keypoints_loss(
self, masks, target_gt_idx, keypoints, batch_idx, stride_tensor, target_bboxes, pred_kpts
):
"""
Calculate the keypoints loss for the model.
This function calculates the keypoints loss and keypoints object loss for a given batch. The keypoints loss is
based on the difference between the predicted keypoints and ground truth keypoints. The keypoints object loss is
a binary classification loss that classifies whether a keypoint is present or not.
Args:
masks (torch.Tensor): Binary mask tensor indicating object presence, shape (BS, N_anchors).
target_gt_idx (torch.Tensor): Index tensor mapping anchors to ground truth objects, shape (BS, N_anchors).
keypoints (torch.Tensor): Ground truth keypoints, shape (N_kpts_in_batch, N_kpts_per_object, kpts_dim).
batch_idx (torch.Tensor): Batch index tensor for keypoints, shape (N_kpts_in_batch, 1).
stride_tensor (torch.Tensor): Stride tensor for anchors, shape (N_anchors, 1).
target_bboxes (torch.Tensor): Ground truth boxes in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format, shape (BS, N_anchors, 4).
pred_kpts (torch.Tensor): Predicted keypoints, shape (BS, N_anchors, N_kpts_per_object, kpts_dim).
Returns:
kpts_loss (torch.Tensor): The keypoints loss.
kpts_obj_loss (torch.Tensor): The keypoints object loss.
"""
batch_idx = batch_idx.flatten()
batch_size = len(masks)
# Find the maximum number of keypoints in a single image
max_kpts = torch.unique(batch_idx, return_counts=True)[1].max()
# Create a tensor to hold batched keypoints
batched_keypoints = torch.zeros(
(batch_size, max_kpts, keypoints.shape[1], keypoints.shape[2]), device=keypoints.device
)
# TODO: any idea how to vectorize this?
# Fill batched_keypoints with keypoints based on batch_idx
for i in range(batch_size):
keypoints_i = keypoints[batch_idx == i]
batched_keypoints[i, : keypoints_i.shape[0]] = keypoints_i
# Expand dimensions of target_gt_idx to match the shape of batched_keypoints
target_gt_idx_expanded = target_gt_idx.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
# Use target_gt_idx_expanded to select keypoints from batched_keypoints
selected_keypoints = batched_keypoints.gather(
1, target_gt_idx_expanded.expand(-1, -1, keypoints.shape[1], keypoints.shape[2])
)
# Divide coordinates by stride
selected_keypoints /= stride_tensor.view(1, -1, 1, 1)
kpts_loss = 0
kpts_obj_loss = 0
if masks.any():
gt_kpt = selected_keypoints[masks]
area = xyxy2xywh(target_bboxes[masks])[:, 2:].prod(1, keepdim=True)
pred_kpt = pred_kpts[masks]
kpt_mask = gt_kpt[..., 2] != 0 if gt_kpt.shape[-1] == 3 else torch.full_like(gt_kpt[..., 0], True)
kpts_loss = self.keypoint_loss(pred_kpt, gt_kpt, kpt_mask, area) # pose loss
if pred_kpt.shape[-1] == 3:
kpts_obj_loss = self.bce_pose(pred_kpt[..., 2], kpt_mask.float()) # keypoint obj loss
return kpts_loss, kpts_obj_loss
v8ClassificationLoss
\[L = -\sum y \log(p)\]class v8ClassificationLoss:
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Compute the classification loss between predictions and true labels."""
preds = preds[1] if isinstance(preds, (list, tuple)) else preds
loss = F.cross_entropy(preds, batch["cls"], reduction="mean")
loss_items = loss.detach()
return loss, loss_items
v8OBBLoss
\[L = L_{box} + L_{cls} + L_{dfl}\]class v8OBBLoss(v8DetectionLoss):
"""Calculates losses for object detection, classification, and box distribution in rotated YOLO models."""
def __init__(self, model):
"""Initializes v8OBBLoss with model, assigner, and rotated bbox loss; note model must be de-paralleled."""
super().__init__(model)
self.assigner = RotatedTaskAlignedAssigner(topk=10, num_classes=self.nc, alpha=0.5, beta=6.0)
self.bbox_loss = RotatedBboxLoss(self.reg_max).to(self.device)
def preprocess(self, targets, batch_size, scale_tensor):
"""Preprocesses the target counts and matches with the input batch size to output a tensor."""
if targets.shape[0] == 0:
out = torch.zeros(batch_size, 0, 6, device=self.device)
else:
i = targets[:, 0] # image index
_, counts = i.unique(return_counts=True)
counts = counts.to(dtype=torch.int32)
out = torch.zeros(batch_size, counts.max(), 6, device=self.device)
for j in range(batch_size):
matches = i == j
if n := matches.sum():
bboxes = targets[matches, 2:]
bboxes[..., :4].mul_(scale_tensor)
out[j, :n] = torch.cat([targets[matches, 1:2], bboxes], dim=-1)
return out
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Calculate and return the loss for the YOLO model."""
loss = torch.zeros(3, device=self.device) # box, cls, dfl
feats, pred_angle = preds if isinstance(preds[0], list) else preds[1]
batch_size = pred_angle.shape[0] # batch size, number of masks, mask height, mask width
pred_distri, pred_scores = torch.cat([xi.view(feats[0].shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in feats], 2).split(
(self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1
)
# b, grids, ..
pred_scores = pred_scores.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_distri = pred_distri.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
pred_angle = pred_angle.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
dtype = pred_scores.dtype
imgsz = torch.tensor(feats[0].shape[2:], device=self.device, dtype=dtype) * self.stride[0] # image size (h,w)
anchor_points, stride_tensor = make_anchors(feats, self.stride, 0.5)
# targets
try:
batch_idx = batch["batch_idx"].view(-1, 1)
targets = torch.cat((batch_idx, batch["cls"].view(-1, 1), batch["bboxes"].view(-1, 5)), 1)
rw, rh = targets[:, 4] * imgsz[0].item(), targets[:, 5] * imgsz[1].item()
targets = targets[(rw >= 2) & (rh >= 2)] # filter rboxes of tiny size to stabilize training
targets = self.preprocess(targets.to(self.device), batch_size, scale_tensor=imgsz[[1, 0, 1, 0]])
gt_labels, gt_bboxes = targets.split((1, 5), 2) # cls, xywhr
mask_gt = gt_bboxes.sum(2, keepdim=True).gt_(0.0)
except RuntimeError as e:
raise TypeError(
"ERROR ❌ OBB dataset incorrectly formatted or not a OBB dataset.\n"
"This error can occur when incorrectly training a 'OBB' model on a 'detect' dataset, "
"i.e. 'yolo train model=yolo11n-obb.pt data=dota8.yaml'.\nVerify your dataset is a "
"correctly formatted 'OBB' dataset using 'data=dota8.yaml' "
"as an example.\nSee https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/obb/ for help."
) from e
# Pboxes
pred_bboxes = self.bbox_decode(anchor_points, pred_distri, pred_angle) # xyxy, (b, h*w, 4)
bboxes_for_assigner = pred_bboxes.clone().detach()
# Only the first four elements need to be scaled
bboxes_for_assigner[..., :4] *= stride_tensor
_, target_bboxes, target_scores, fg_mask, _ = self.assigner(
pred_scores.detach().sigmoid(),
bboxes_for_assigner.type(gt_bboxes.dtype),
anchor_points * stride_tensor,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
mask_gt,
)
target_scores_sum = max(target_scores.sum(), 1)
# Cls loss
# loss[1] = self.varifocal_loss(pred_scores, target_scores, target_labels) / target_scores_sum # VFL way
loss[1] = self.bce(pred_scores, target_scores.to(dtype)).sum() / target_scores_sum # BCE
# Bbox loss
if fg_mask.sum():
target_bboxes[..., :4] /= stride_tensor
loss[0], loss[2] = self.bbox_loss(
pred_distri, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask
)
else:
loss[0] += (pred_angle * 0).sum()
loss[0] *= self.hyp.box # box gain
loss[1] *= self.hyp.cls # cls gain
loss[2] *= self.hyp.dfl # dfl gain
return loss.sum() * batch_size, loss.detach() # loss(box, cls, dfl)
def bbox_decode(self, anchor_points, pred_dist, pred_angle):
"""
Decode predicted object bounding box coordinates from anchor points and distribution.
Args:
anchor_points (torch.Tensor): Anchor points, (h*w, 2).
pred_dist (torch.Tensor): Predicted rotated distance, (bs, h*w, 4).
pred_angle (torch.Tensor): Predicted angle, (bs, h*w, 1).
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): Predicted rotated bounding boxes with angles, (bs, h*w, 5).
"""
if self.use_dfl:
b, a, c = pred_dist.shape # batch, anchors, channels
pred_dist = pred_dist.view(b, a, 4, c // 4).softmax(3).matmul(self.proj.type(pred_dist.dtype))
return torch.cat((dist2rbox(pred_dist, pred_angle, anchor_points), pred_angle), dim=-1)
E2EDetectLoss
\[L = L_{one2many} + L_{one2one}\]class E2EDetectLoss:
"""Criterion class for computing training losses."""
def __init__(self, model):
"""Initialize E2EDetectLoss with one-to-many and one-to-one detection losses using the provided model."""
self.one2many = v8DetectionLoss(model, tal_topk=10)
self.one2one = v8DetectionLoss(model, tal_topk=1)
def __call__(self, preds, batch):
"""Calculate the sum of the loss for box, cls and dfl multiplied by batch size."""
preds = preds[1] if isinstance(preds, tuple) else preds
one2many = preds["one2many"]
loss_one2many = self.one2many(one2many, batch)
one2one = preds["one2one"]
loss_one2one = self.one2one(one2one, batch)
return loss_one2many[0] + loss_one2one[0], loss_one2many[1] + loss_one2one[1]
NMS
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False, multi_label=False,
labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output